Scientists Move A Step Closer To Drought-Tolerant Soybean Variety
- News
- 2.2K
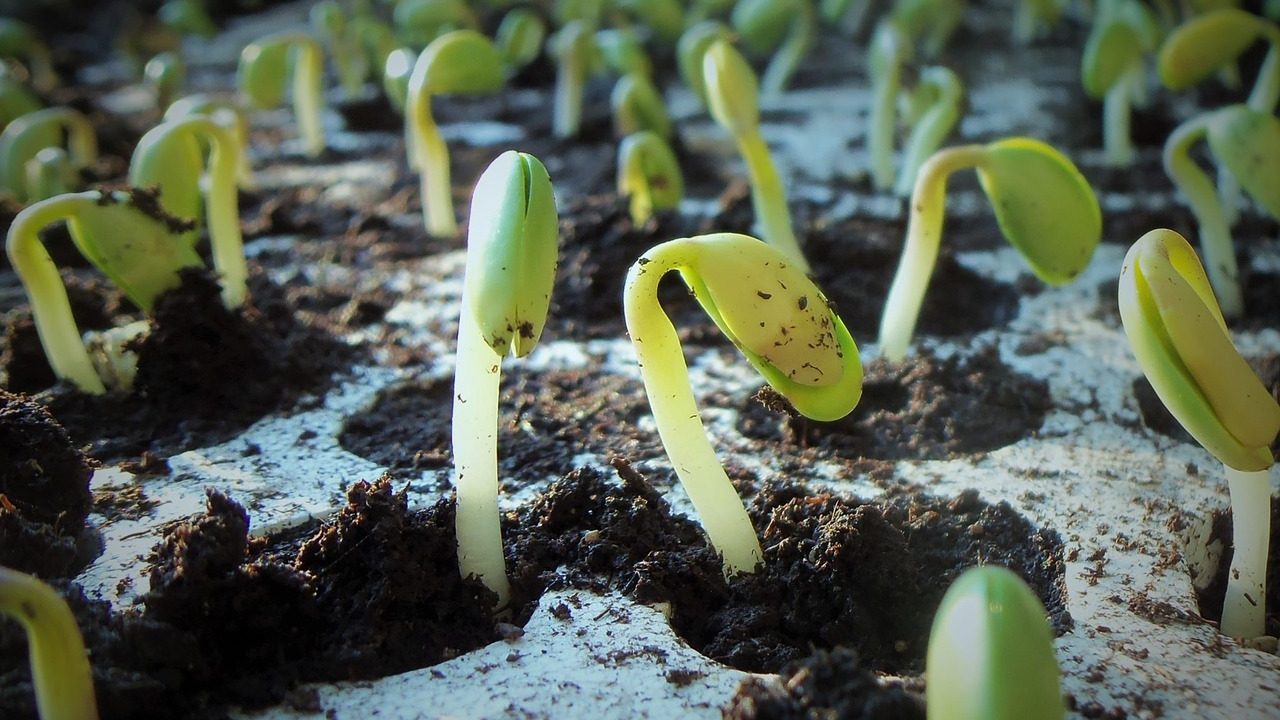
The productivity of soybean, an important oilseed crop, is severely affected due to droughts. A team of Indian scientists has now identified genotypes of soybean that can tolerate drought better without comprising on yields. By incorporating the traits which confer drought tolerance in these cultivars, scientists hope to develop more resilient varieties.
The recurrent droughts pose a threat to food security as over sixty percent of the country’s net sown area depends on rainfall for agriculture. Soybean is grown mainly under rainfed conditions due to which drought at any stage of the plant’s growth could adversely hit soybean productivity.
Scientists at the Indore-based Indian Institute of Soybean Research studied sixteen genotypes of soybean while searching for drought-tolerant traits. In this experiment which was conducted in the institute campus at Indore, sixteen genotypes were grown in normal irrigated conditions until they reached the reproductive stage. Thereafter, experimental plants were deprived of water while another set of plants were given normal irrigation.
Scientists then measured various parameters like canopy temperature, root length, specific leaf weight, photosynthetic rate, chlorophyll, and epicuticular wax content of the genotypes grown in both irrigated and water deprived conditions.
Researchers found a significant decline in seed yield which ranged from 20 to 62% depending on the genotype. Based on the low decline in productivity, four soybean genotypes (EC 538828, JS 97-52, EC 456548, and EC602288) were considered to be resistant to drought.
It was found that traits like low canopy temperature, longer roots, high root/shoot weight ratio, high specific leaf weight, chlorophyll content and photosynthetic rate, seen in drought tolerant genotypes, are associated better seed yields in drought conditions.
Most importantly, a longer root system was found to be most correlated to drought resilience as it allowed the plant to mine water and nutrients from the soil efficiently under drought conditions. The wax content in leaves, which prevents water loss due to transpiration, was also found to be positively correlated to avoidance in drought conditions.
“These traits and genotypes can be utilized in a breeding program aimed at developing soybean varieties tolerant to drought stress,” explained Dr. Virender Singh Bhatia, leader of the research group, while talking to India Science Wire.
The study results have been published in the journal Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants. The research team included also Kanchan Jumrani. (India Science Wire)
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for the latest Science & Tech news. You can also find us on Twitter & Facebook.