Gandhi: Fitness Freak, Champion of Sustainable Food and A Pioneering Vegan
- News
- 1.6K
Walking and engaging in physical activity every day, a good intake of fresh vegetables and fruits, consuming food items low in sugars, salt and fats, avoid taking tobacco and alcohol, maintaining environmental cleanliness and personal hygiene.

This may sound pretty much like advisory issued by the World Health Organisation to keep non-communicable as well as communicable diseases at bay. But these are actually the tenets of good health Mahatma Gandhi preached and practiced a century ago.
Many of these ideas, feel nutritionists and public health experts, are greatly relevant now and have the backing of scientific evidence. They can help fight health problems ranging from malnutrition to heart disease.
Gandhi believed that excessive eating, too frequent meals and overindulgence of concentrated starches and sugars were unhealthy and caused diseases. He suggested avoiding sweets as much as possible and consuming jaggery in small quantities.
He was against polishing of rice or refining of wheat flour. “Sieving of the flour should be avoided. It is likely to remove the pericarp which is a rich source of salts and vitamins, both of which are most valuable from the point of view of nutrition,” he had written.
“All this is in tune with the current recommendations on nutrition,” nutritionists Subbarao M. Gavaravarapu and R. Hemalatha from the Hyderabad-based National Institute of Nutrition (NIN) have observed in an analysis published in a special issue of the Indian Journal of Medical Research (IJMR). “Gandhiji recognized the need for including fats/oils in the diet. Even today, the Dietary Guidelines developed by NIN suggest that about 10% of the total daily calories should be met from visible fats.”
The remarkable aspect of some of Gandhi’s diet recommendations is that they are relevant even today, the researchers have observed. “Today, beset as we are with lifestyle diseases driven by our faulty food choices and sedentary habits, ‘locally grown’, ‘less oil and salt’, ‘less sugary,’ ‘farm fresh’, ‘low fat’ have become much-bandied words.
Nutrition science extols the virtues of fresh vegetables and fruits, the probiotic potential of curds or yogurt and decries ill-effects of sugar and refined flours. The virtues of walking, regular exercise, and good sanitary habits are all important. These were the very by-words that Gandhi lived by,” the paper has concluded.
Through his interaction with scientists, Gandhi exchanged knowledge and even influenced medical research in British India to some extent. Robert McCarrison, the first Director of NIN, used to have long conversations with Gandhi on diet and dietetics, particularly on the use of milk as Gandhi had taken a vow not to drink milk. “That relationship resulted in creating a strong foothold in the area of nutrition and accelerating research,” pointed out Dr. Balram, Bhargava, director general of the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
In the field of communicable disease, Gandhi emphasized the importance of eliminating mosquito breeding sites and regular monitoring of water containers as a measure to prevent breeding of mosquitoes and malaria. He considered such methods more effective than the distribution of quinine tablets. Gandhi also sought elimination of diseases like leprosy and tuberculosis that bred stigma and untouchability through isolation of those infected.
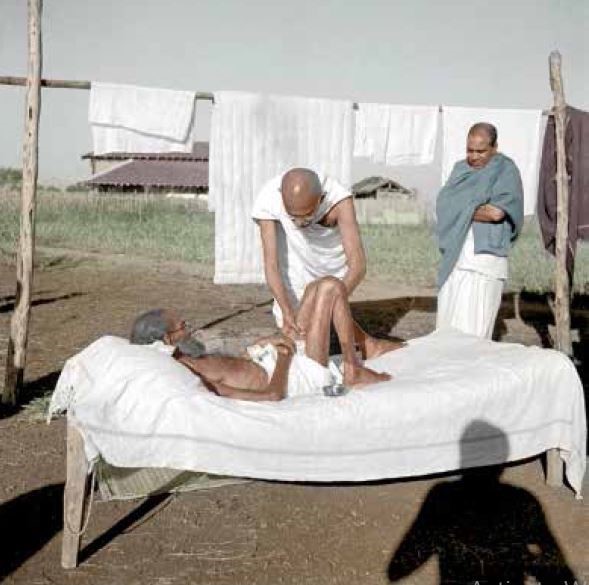
Gandhi was a fitness freak. He walked around 18 km every day for nearly 40 years. During his political campaigns from 1913 to 1948, he walked a total of 79,000 km, which is equivalent to walking around the earth twice, according to his health records published in the journal. Yet he struggled with several health issues – pleurisy (1914), malaria (1925, 1936 and 1944), gastric flu (1939) and influenza (1945). He was operated on for piles (1919) and severe appendicitis (1924). But he was back on his feet every time, largely due to his disciplined lifestyle which included focusing on physical fitness and a balanced diet.
“Although Gandhiji was never against allopaths, vaidyas, and hakims, his preference lay with naturopathic medicines. He often said that naturopathy was his hobby. He argued that if a disease was a result of breaking nature’s law, nature would be able to rectify it. He practiced naturopathy for more than fifty years,” Dr. Bhargava has noted. “He was not partial towards any system but believed in the power of preventive care and treatment for all.” (India Science Wire)
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for the latest Science & Tech news. You can also find us on Twitter & Facebook.