Biomass of Invasive Weed Can Help Treat Toxic Waste
- News
- 1.7K
Prosopis Juliflora is an invasive weed with an abundant spread in India. Called Seemai Karuvelam in Tamil and Vilayati Babul in Hindi, it has outstanding capability to survive and grow on dry arid and saline lands.
Scientists at the Indian Institute of Technology, Madras have developed a method to make a low-cost adsorbent using the weed and apply that to treat toxic effluents. The technology converts the weed into activated carbon, which, in turn, removes organic compounds, phosphate, and nitrate from polluted water.
“Synthesis of activated carbon using Prosopis Juliflora biomass is economical and can be used to reduce the overall cost of the treatment process. This can improve management of the invasive plant and simultaneously protect the environment,” explained Dr. S. Mathava Kumar, Associate Professor in the Department of Civil Engineering at IIT Madras, while speaking to India Science Wire.
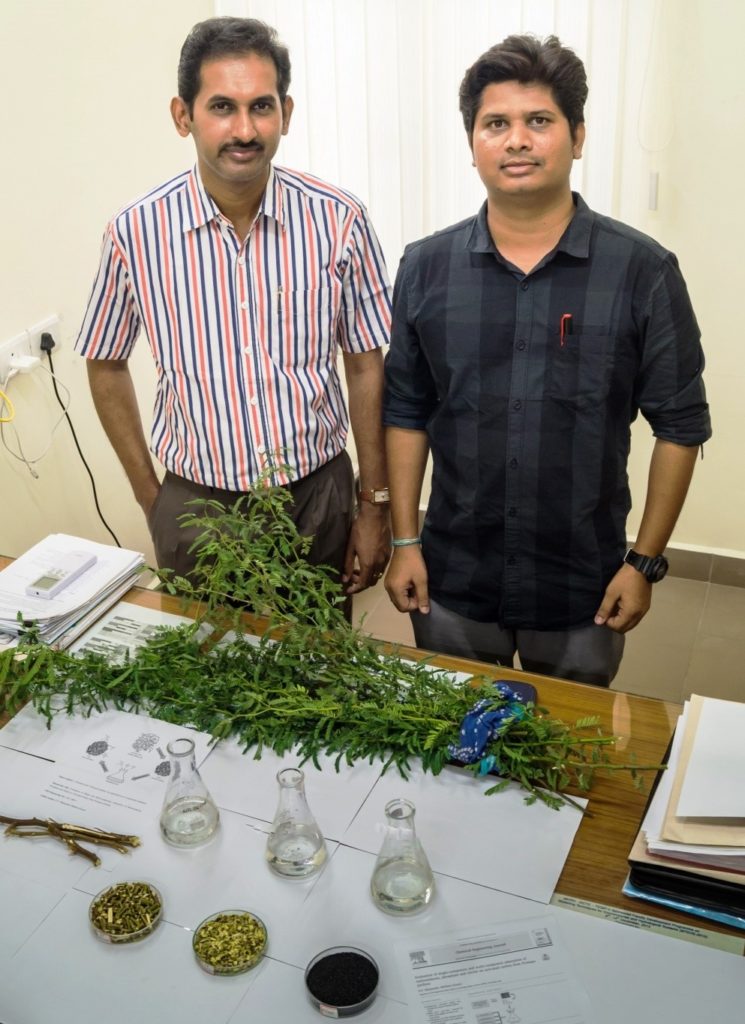

Researchers at IIT Madras
The team collected the weed from within the institute campus, where it is available in plenty. They cleaned, shredded the twigs to one-centimeter size and allowed it to dry. They then processed this feedstock and converted it into carbon at 500-degree temperature, and further activated it with sulfuric acid.
The researchers studied surface characteristics of the prepared activated carbon using scanning electron microscopy with electron diffraction analysis. They also analyzed its carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur composition using CHNS analyzer. They confirmed the presence of functional groups using Fourier transformation-infrared radiation (FTIR) analysis, and the structure of the product by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis.
It was found that the Prosopis Juliflora activated carbon was effective in removing traces of organic substance like metronidazole, nutrients like phosphates and nitrates in both single-component and multi-component adsorption systems. In addition, septic tank effluents containing trace organics such as antibiotics and essential soil nutrients are trapped onto the surface of the activated carbon, thereby preventing pollutants from entering into the groundwater or surrounding aquifers.
The adsorbent can be used in the tertiary treatment of wastewater at the sewage treatment plants and in soak-pits connected to septic tanks of residential houses, apartments, schools, and hospitals said the scientists.
“After the adsorption process for nutrient removal, the recovered Prosopis juliflora activated carbon, which is rich in nutrients, can be applied to the agricultural fields, which in turn will improve the soil nutrients, thereby increase the crop production and reduce the usage of chemical fertilizers”, commented co-researcher S.V. Manjunath.
According to the United Nations World Water Development Report 2017, over 80 percent of wastewater is discharged without treatment globally. The conventional treatment systems designed are observed to be under-performing in the removal of these trace organics. The new research assumes importance in this context.
The team is carrying out further investigations for the surface modification of the new activated carbon material to see if its adsorption capacity could be further improved. The results of the research have been published in the journal Chemical Engineering. (India Science Wire)
By Dr. Sanghamitra Deobhanj
Journal Article
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for the latest Science and Tech news. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.


