Indian Darjeeling Tea Faces Climate Risk
- News
- 5.4K
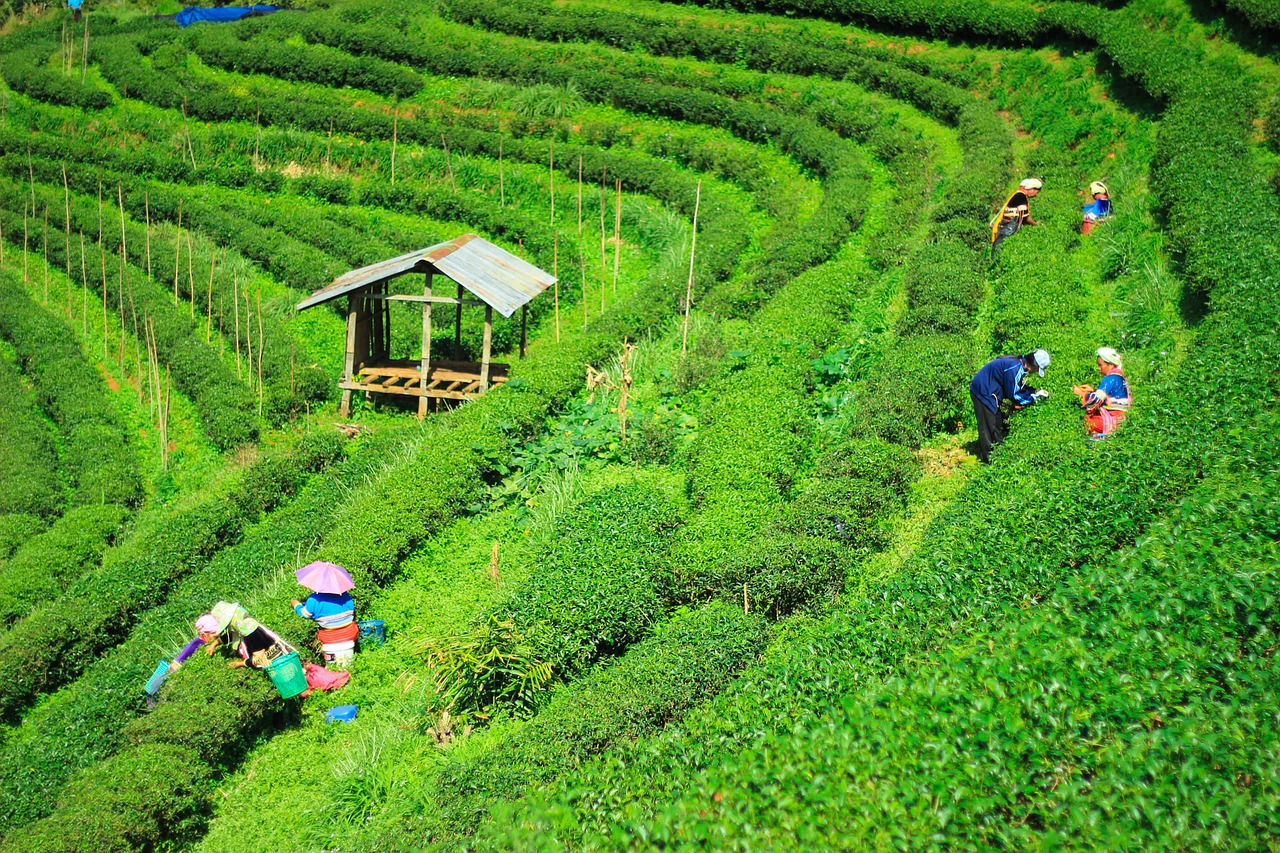
A gradual change in temperature and rainfall patterns in Darjeeling hills is beginning to affect the production of the famous Darjeeling tea.
The maximum temperature in Kurseong has risen by 0.51 degree over the last 20 years while total annual rainfall dropped by 56 mm and relative humidity by 16.07 %, leading to a decline in overall production of Darjeeling tea in terms of green leaf production per hectare.
This has emerged from studies conducted at the experimental farms of the Darjeeling Tea Research and Development Centre (DTR&DC) at Kurseong to see the effect of climate change on production of tea.
The West Bengal State Climate Action Plan has also expressed concern over “reduced productivity of Darjeeling tea due to increase in extended drought periods.” In other hill regions in the state, the plan has reported a decline in size and quality of citrus fruits like mandarin orange as a result of rising minimum temperature during the flowering season.
Tea is a rain-fed crop that needs specific soil and air temperature as well as moisture condition for desired growth. Both increased temperatures and decreasing rainfall – along with a change in relative humidity – adversely affect quantity and quality of tea production. The chances of pest infestation also go up with the increase in temperature.
The ideal temperature for growing tea is between 18 and 30 degrees. The plant growth is adversely affected when the temperature goes above 32 degrees or drops below 13 degrees. In addition, strong winds, frequent frost, hail, and excessive rainfall are also detrimental for production of high-quality tea.
“Both excess and shortage of water affect the growth of tea bushes. Tea bushes need adequate and well-distributed rainfall. Heavy and erratic rainfall can damage tea plantation due to soil erosion, lack of growth due to fewer sunshine hours and different types of insect pest and diseases, besides flooding,” explained Mrityunjay Choubey, the researcher from DTR&DC, while speaking at a media workshop on climate change here last week.
Tea is grown in five different valleys in the region – Darjeeling, Mirik, Teesta, Rambang, and Kurseong – each having different elevation and weather pattern.
“There is no doubt that rainfall has come down drastically in all the valleys. But we have to collate data from all the stations, including those run by the India Meteorological Department and also analyze other factors such as the shift from inorganic to organic farming and levels of absenteeism, before we can pinpoint reasons for falling production. Climate change may be one of the factors,” pointed out Prahalad Chetri, project director of the R&D center, Tea Board of India, while speaking to India Science Wire.
Choubey, however, said that since the experimental farm followed the inorganic method of cultivation, yield reduction could not be attributed to shifting from inorganic to organic cultivation practices. “The probable reason (for yield reduction) may be temperature rise, lack of total as well as the distribution of rainfall and less humidity. These factors affect carbohydrate assimilation, respiration, and evapotranspiration of tea plants, pest and disease infestation, drought and heavy rainfall incidence and soil degradation,” he added.
In view of this, he said, it was critical to identify and evaluate options for adaptation to future climate change. Adaptation measures will include the use of drought-tolerant clones, reducing chemical load by integrated nutrient management. Organic farming is highly adaptable to climate change as it preserves inherent soil fertility and maintains organic matter in soils which can sustain productivity in the event of drought or irregular rainfall.
The workshop was jointly organized by Indian Himalayas Climate Adaptation Programme (IHCAP), Department of Science and Technology (DST) and Centre for Media Studies (CMS). (India Science Wire)
By Dinesh C Sharma
For the latest Science, Tech news and conversations, follow Research Stash on Twitter, Facebook, and subscribe to our YouTube channel