NIOT Develops Rapid PCR Kit to Detect Multi Drug Resistant Bacteria
- News
- 1.8K
Scientists at the National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT), Port Blair, have developed a highly effective kit to detect the multi-drug-resistant (MDR) strains of the gram-positive bacteria Enterococcus faecalis. This tool would enable rapid detection of the virulence of the pathogen in a single step, which would be an important tool not only in the healthcare system but also in anti-bioterrorism measures and environmental monitoring applications.
The result of the study published in the Journal of Microbiological Methods states that the tool would be useful to the food industries where it can be used to maintain the quality and safety of seafood as well as to easily detect the bacteria in the herds of cattle used for milk and thus making the milk products safe.
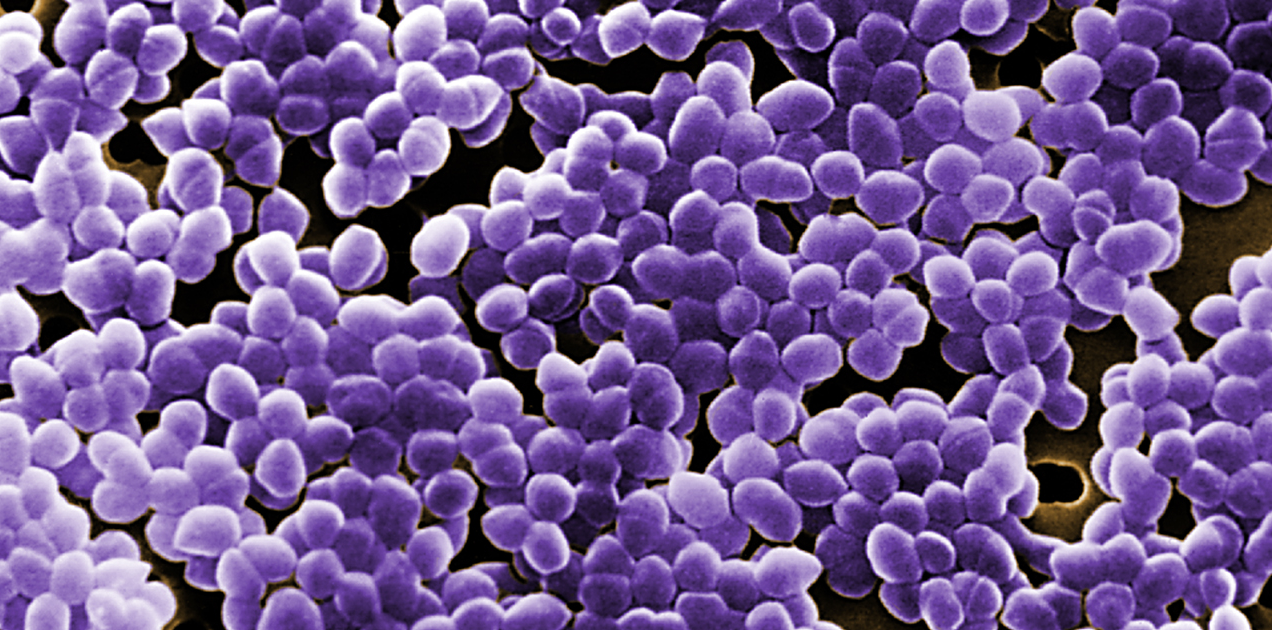
Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis) is a group of gram-positive bacteria that are a common cause of morbidity and motility across the world infecting the urinary tract, bloodstream, endocardium, abdomen, biliary tract, burn wounds, and indwelling foreign devices. These infections can be exceptionally difficult to treat because of the drug resistance of many E. faecalis isolates.
E. faecalisreaches humans from the food chain, mainly through sewage or non-sewage systems. Environmental waters such as agricultural fields, coastal waters, agricultural wells, clinical samples, marine sediment, rivers, and canals are the common source of E. faecalis and E. faecium contamination. These are fecal bacteria that spread rapidly from solid waste passed out of the body of humans or animals. About 90% of the enterococcal (éntero in Greek meaning “intestine” and coccus meaning “granule”) infections in humans are caused by E. faecalis.
By-products obtained from treated sewage wastewater, which are used as fertilizers in the agricultural fields, can be potential sources of multi-drug-resistant strains of E. faecalis, which can easily get entered into the food supply chain. Till now detection and early diagnosis of these bacteria were very time-consuming.
With the development of this multiple Polymer Chain Reaction (PCR) kit, which is highly specific in detecting the disease-causing virulent genes present in the E. faecalis bacteria, namely, gelE (gelatinase), hyl (hyaluronidase), and asa1 (aggregation substance), the rapid detection of the bacteria became possible. In addition to this, the NIOT researchers validated the testing protocol of the PCR kit by using 243 different E. faecalis strains from potentially contaminated sources like marine sediment, marine water, seafood sample, cattle fodder, freshwater sample as well as clinical samples to see the efficacy of rapid detection.
The aggregation of asa1 on the surface of E. faecalis increases the hydrophobicity of E. facecalis cell surface and make the bacteria more stable against antibiotics. The other group of hydrolytic enzymes includes hyaluronidase and gelatinase which also increase the virulence of E. species. For example, hyaluronidase is a degradative enzyme that damages the host tissues facilitating the spread of enterococci as well as their toxins. E. faecalis secretes GelE, which can hydrolyze gelatin, casein, hemoglobin, and other bioactive peptides damaging the host tissues leading to microbial disease.
The authors of the present work stated that the new PCR-based specific bacterial gene diagnostic tools can detect bacteria faster than the traditional method. In the traditional method, bacterial strains are required in higher concentrations involving expensive evaluation techniques and highly trained experts can only evaluate a contaminated sample which is time-consuming. However, this multiple PCRs detection kit developed by NIOT Port Blair is highly sensitive even at a very low concentration of E. faecalis strains to detect the disease-causing genes specific to this specific bacterium.
The new technology developed by NIOT would be very useful in many of the Southeast Asian countries where septic tanks are widely used which are active sources of pathogen dispersal to the groundwater as doubtful contaminated samples can be tested for contamination rapidly and thus bring out policies to build a legal framework to stop the pathogen dispersal effectively.
Led by B. Meena, and L. Anburajan the research team comprised of N. V. Vinithkumara of NIOT, Port Blair, Ministry of Earth Sciences, K. S. Varma of SAAI Electro Biogenic India Pvt. Ltd., Ponneri, Chennai, and R. Kirubagaran, G. Dharani of NIOT, Chennai. (ISW)
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for the latest Science & Tech news. You can also find us on Twitter & Facebook


