New Method Makes Cancer Drugs Less Toxic
- News
- 1.7K
New Method for Controlled-Release Makes Cancer Drugs Less Toxic to Healthy Tissues
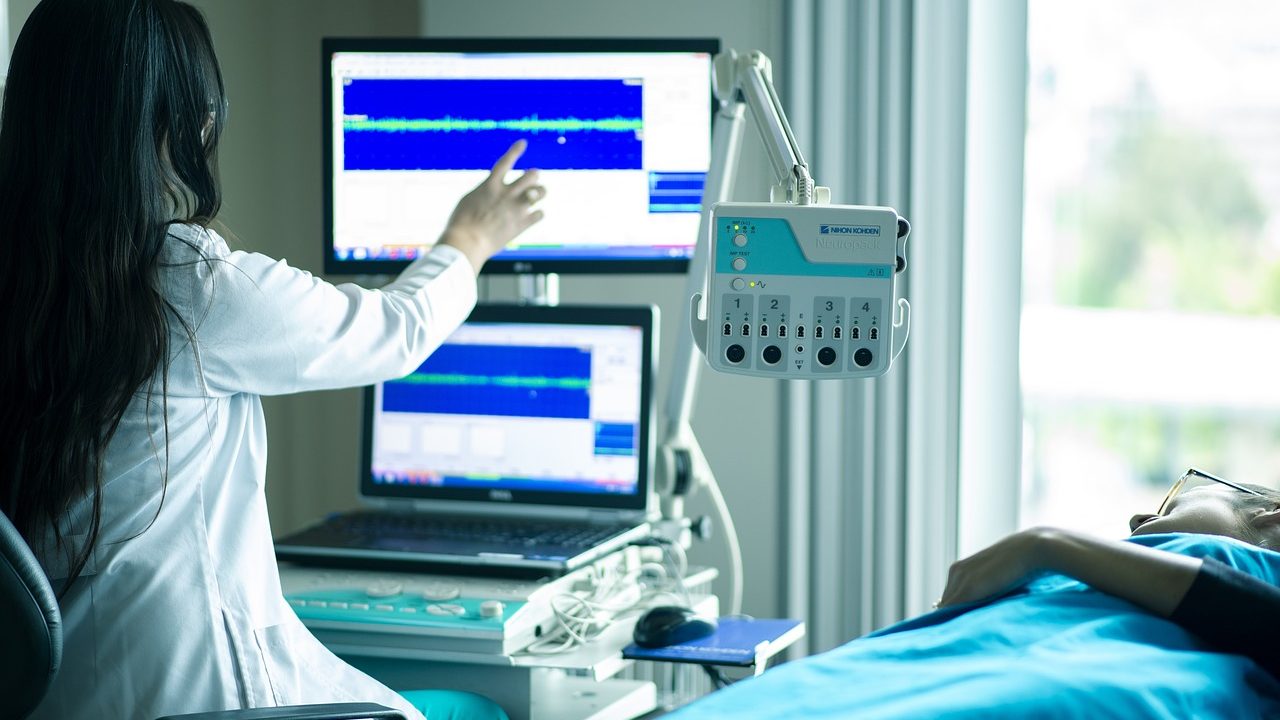
Chemotherapy is one of the most widely used treatments for cancer. It involves a single or combination of drugs that prevent cancer cells from dividing and growing. Most cancer patients who have to undergo chemotherapy treatment worry about the associated adverse side effects caused to healthy cells.

Scientists have been working to find ways to minimise side effects while maintaining the effectiveness of chemotherapy. A group of Indian researchers have now developed a hydrogel-based cancer treatment method.
In conventional chemotherapy, drugs being administered get diffused immediately resulting in an uncontrolled and unpredictable pattern of drug release. This burst of the drug causes damage to surrounding healthy cells. To overcome this problem, researchers have developed a superstructure of cyclodextrin and polyurethane polymer. It acts as a drug depot and releases the drug in a slow and controlled manner, increasing its efficiency.
This superstructure has been found to be friendly to biological tissues when tested in animals with an anti-cancer drug, paclitaxel. It could treat skin cancers much better when compared to the pure drug as given in chemotherapy. No side effects were observed in various biochemical parameters and histopathological tests.
“We have designed three generations of the hyperbranched structure of polymer using hydrophilic cyclodextrin and wrapped up using hydrophobic polyurethane through grafting. This special architecture handles drug release in a controlled manner.
The drug is available for its action even after three days of administration into the bloodstream as opposed to burst release of drug in conventional chemotherapy,” explained Professor Pralay Maiti of IIT (BHU), who led the research, while speaking to India Science Wire.
Injectable hydrogel solution once injected inside the body turns into solid which enhances its efficiency by localising at the tumour site. The drug and polymer superstructure interact and the balance between actions of its hydrophilic and hydrophobic layers ensures slow drug release, researchers said.
“We would like to apply this knowledge for patient care and have already filed patents. We are also trying to cure other cancers like breast, colon and other vital organ tumours,” said Prof. Maiti.
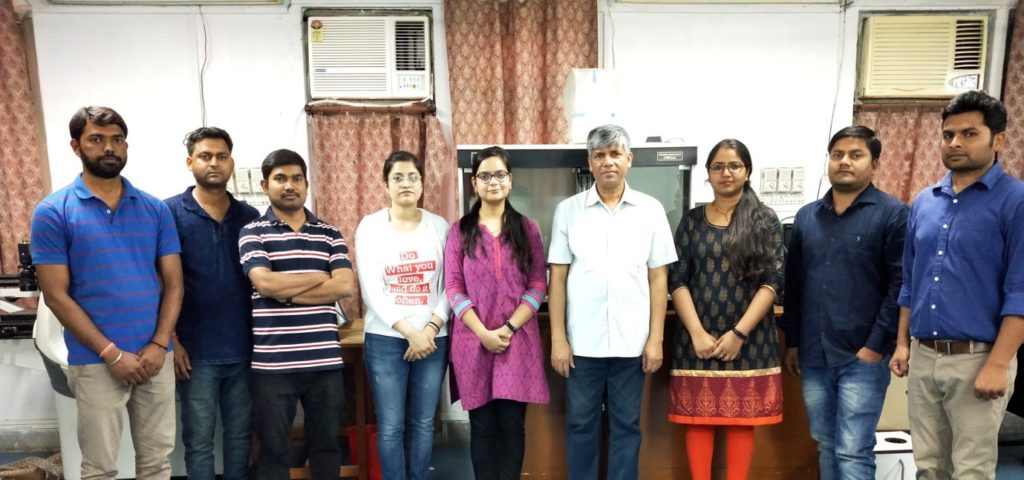
The research team included Prof. Pralay Maiti, Aparna Shukla, Akhand Pratap Singh, Tarkeshwar Dubey and Siva Hemalatha from IIT (Banaras Hindu University). The results of their research have been published in the journal ACS Applied Bio Materials. (India Science Wire)
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for the latest Science & Tech news. You can also find us on Twitter & Facebook.