Researchers Quantify Damage Caused By Peafowls to Farmers
- News
- 1.7K
India’s national bird, Peafowl, has been a part of mythical stories and is also considered sacred. Over centuries, they have been playing an important role in agricultural ecosystems by aiding in seed dispersal, scavenging, and for control of insects and rodents.

However, of late, they are turning out to be a problem. The main issue is that their population is growing. While social customs bar people from causing any harm to them, there has been a decline in the population of its natural predators for various reasons. It is also protected under the Indian Wildlife Act.
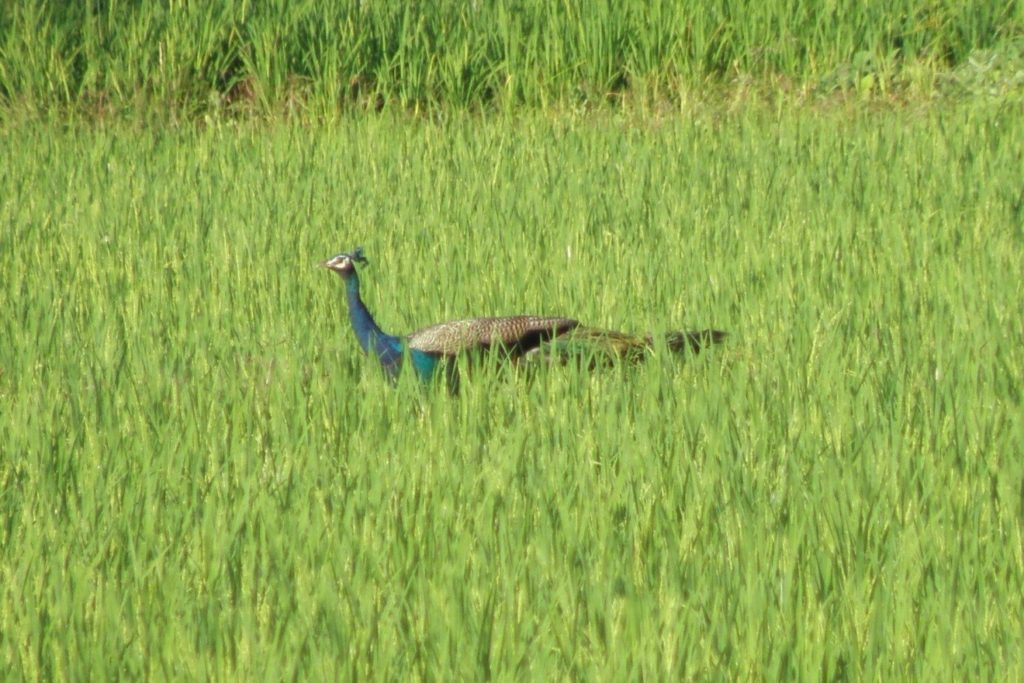
Farmers are hit hardest as instead of being a help peafowls are becoming a menace damaging crops, over-feeding on fruits and grains and trampling on and dislodging seedlings. Consequently, there have even been reports of farmers resorting to poisoning, trapping, hunting, and even electrocution in a surreptitious manner to protect their earnings.
A team of researchers from Kerala Forest Research Institute and Christ College in Thrissur in Central Kerala has sought to find out whether it was possible to pay compensation to the farmers affected by the problem like it is done for damages caused by wild animals like elephants.
They conducted the study at Chulannur Peafowl Sanctuary in the State. They did an enclosure experiment in a paddy field to estimate the loss. They selected two sets of plots, one was provided with an enclosure to avoid depredation by peafowl and other was treated as a control plot. After four years of repeated estimates, the researchers have concluded there can be a difference in the yield of up to 40% on average between the two plots.
The researchers feel that the quantification of actual economic loss could form the basis for the provision of compensation for the farmers. They feel that it can be a win-win situation for all and bringing in the communities into wildlife conservation.
Ex-gratia payment for damage caused by elephants and other wild animals has been a good solution to address the man-animal conflict issues relating to the wildlife. It had not been possible for damage caused by peafowls as there was no data to go by so far.
The study was conducted by Suresh K. Govind of the Forest Research Institute and E. A. Jayson of the Christ College. The study has been published in journal Indian Birds. (India ScienceWire)
By S Suresh Ramanan
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for the latest Science & Tech news. You can also find us on Twitter & Facebook.