Research Stash Weekly Review #28
- Weekly Review
- 2.1K
Weekly Review #28 – Summary of the latest news in science and technology research across the world, carefully handpicked by team Research Stash
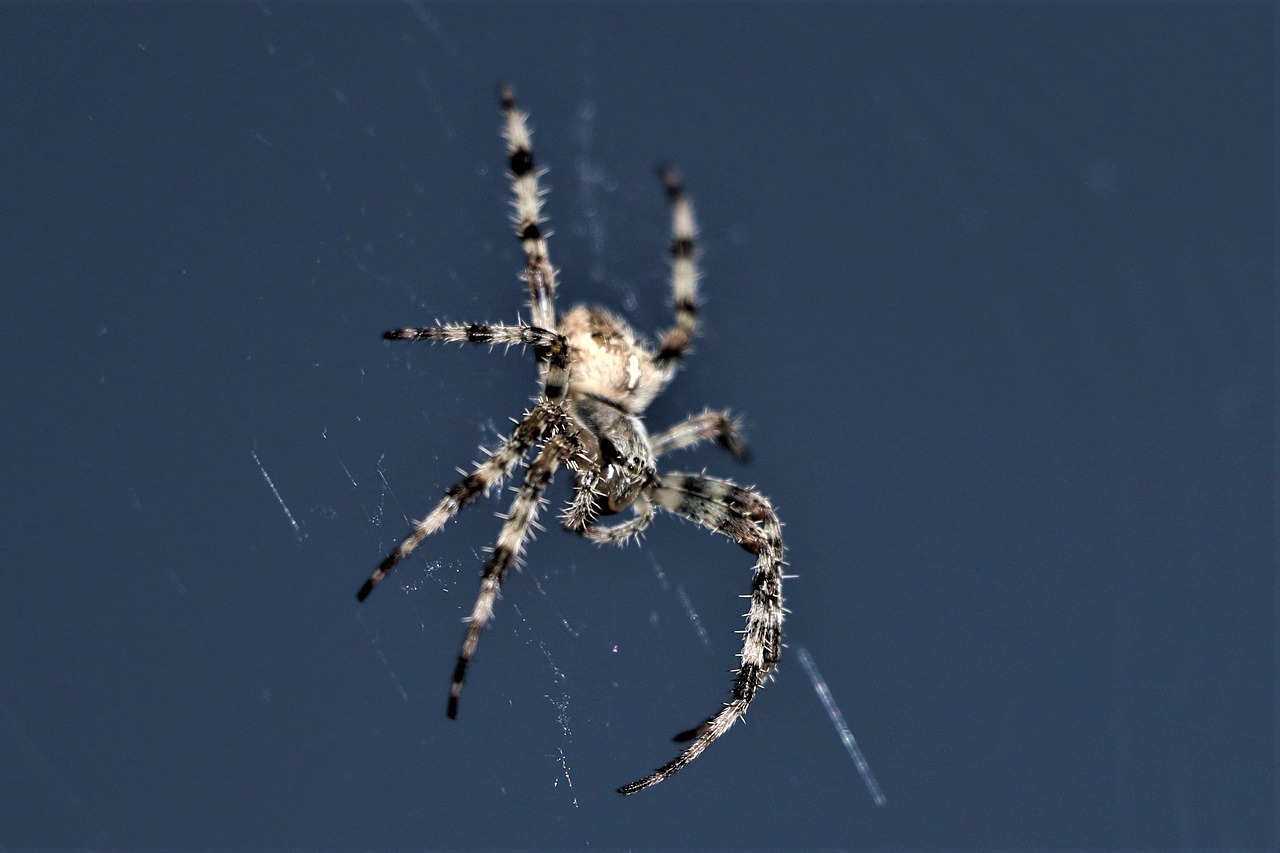
Study Pinpoints The Time You’re Most Likely to Encounter a Spider in Your House, And It Explains a Lot
The researchers, from the University of Gloucestershire and the Charles Darwin House, created a free app called ‘Spider in da House’ (lol) back in August 2013 for the general population to track any run-ins with spiders. Read More
Genes are key to academic success, says study
A study explains the substantial influence genes have on academic success, from the start of elementary school to the last day of high school. Read More
Scientists Create Immature Human Eggs From Stem Cells
Scientists say they have taken a potentially important — and possibly controversial — step toward creating human eggs in a lab dish. Read More
Your gut is directly connected to your brain, by a newly discovered neuron circuit
The human gut is lined with more than 100 million nerve cells—it’s practically a brain unto itself. And indeed, the gut actually talks to the brain, releasing hormones into the bloodstream that, over the course of about 10 minutes, tell us how hungry it is, or that we shouldn’t have eaten an entire pizza. Read More
Scientists create human esophagus in stem cell first
For the first time, researchers have managed to create a human esophagus in the laboratory. This may pave the way for new, regenerative treatments. Read More
Humans have skeletal stem cells that help bones and cartilage grow
Scientists found the stem cells, which give rise to bones, cartilage and the spongy bone that harbors bone marrow, in fetal bones, adult bones and fat, researchers report online September 20 in Cell. Read More
Scientists crack the genetic code of cane toad
A group of scientists from UNSW Sydney, the University of Sydney, Deakin University, Portugal and Brazil has unlocked the DNA of the cane toad, a poisonous amphibian that is a threat to many native Australian species. The findings were published in academic journal GigaScience today. Read More
Scientists identify three causes of Earth’s spin axis drift
Using observational and model-based data spanning the entire 20th century, scientists have for the first time have identified three broadly-categorized processes responsible for Earth’s spin axis drift — contemporary mass loss primarily in Greenland, glacial rebound, and mantle convection. Read More
Astronomers Spot Unprecedented Glow Around Neutron Star
Scientists using the Hubble Space Telescope have glimpsed a neutron star unlike any seen before. Read More
Intestinal bacteria produce the electric current from sugar
Intestinal bacteria can create an electric current, according to a new study from Lund University in Sweden. The results are valuable for the development of drugs, but also for the production of bioenergy, for example. Read More
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for the latest Science & Tech news. You can also find us on Twitter & Facebook.