Early Sowing Can Increase Cotton Yield
- News
- 2.3K
Crop forecasting—prediction of crop production under different weather conditions through computer simulations— can guide decisions to maximize production under a particular weather condition. Such predictions have become important under the emerging climate change scenario where knowledge about the impact of changing weather patterns on crop productivity can help in minimizing yield loss.
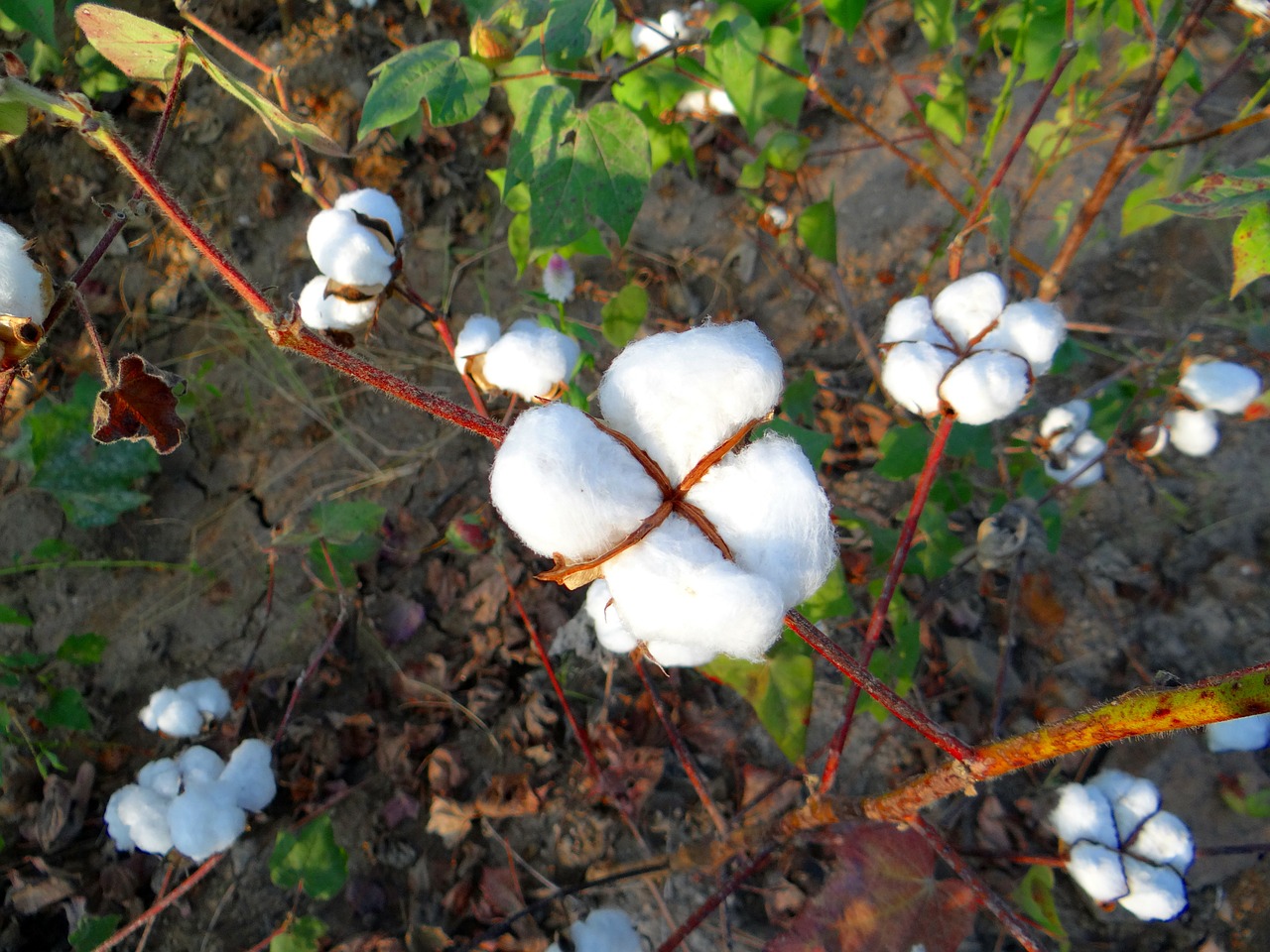
A team of Indian scientists, in their study published in journal Current Science, have predicted that the yield of cotton can be maximized if the crop is sown early (by mid-May) and irrigated during ball formation and maturity stages in case of drought conditions. They identified the stages of cotton plant sensitive to water availability by simulation techniques.
The study involved analyzing rainfall patterns from June to September from 2002 to 2014, which included two drought years (2002, 2014) and two excess rainfall years (2010, 2013). Researchers then collected yield data of three Bt cotton varieties – Pancham-541, RCH-791, and SP-7007, which were cultivated in Hisar district of Haryana, during the Kharif season of these four years.
It was found, through simulations, that early sowing (Mid- May) always yielded better cotton production as compared to late sowing (June). Further, it emerged that irrespective of sowing time, irrigation at ball formation stage (66 to 101 days after sowing) and again at ball maturation stage (101-135 days) can increase the yield in case of drought condition.
“With changing the climate, cotton crop production is affected which has corresponding socio-economic impacts. This can be alleviated with help of improved irrigation support and pest control management”, explained Dr. A. P Dimri, author of the study and Professor at Jawaharlal Nehru University.
Water availability is one of the prime factors that determine crop production. However, it is not economical to go for irrigation throughout the season. Consequently, such studies which help in understanding the critical stages of water required for a particular crop are essential to make better decisions in times of water scarcity.
The research team included A. Shikha (Jawaharlal Nehru University), P. Maharana (University of Delhi), K. K. Singh (India Meteorological Department) and R. Niwas (Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University), besides Dr. Dimri. (India Science Wire)
By Dr. Aditi Jain
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for the latest Science & Tech news. You can also find us on Twitter & Facebook.