Rare basalt columns found in village of Kolhapur
- News
- 3.8K
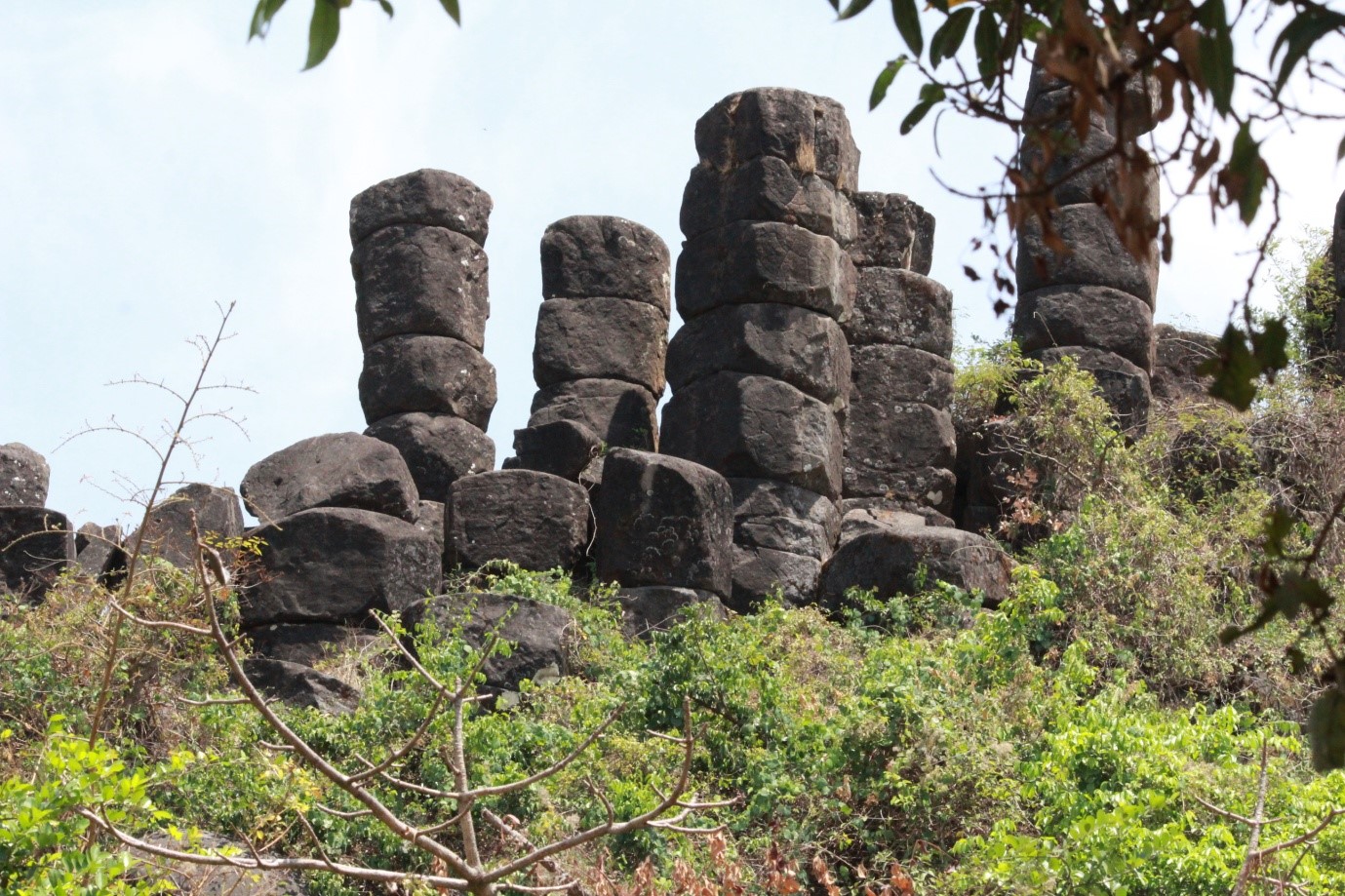
Deccan traps are one of the largest volcanic features on the earth. Polygonal patterns and columnar joints in basaltic rocks are the most fascinating structures for geologists and volcanologists. Now Indian scientists have discovered a rare, well developed polygonal column basalt structure in a village in Kolhapur district in Maharashtra.
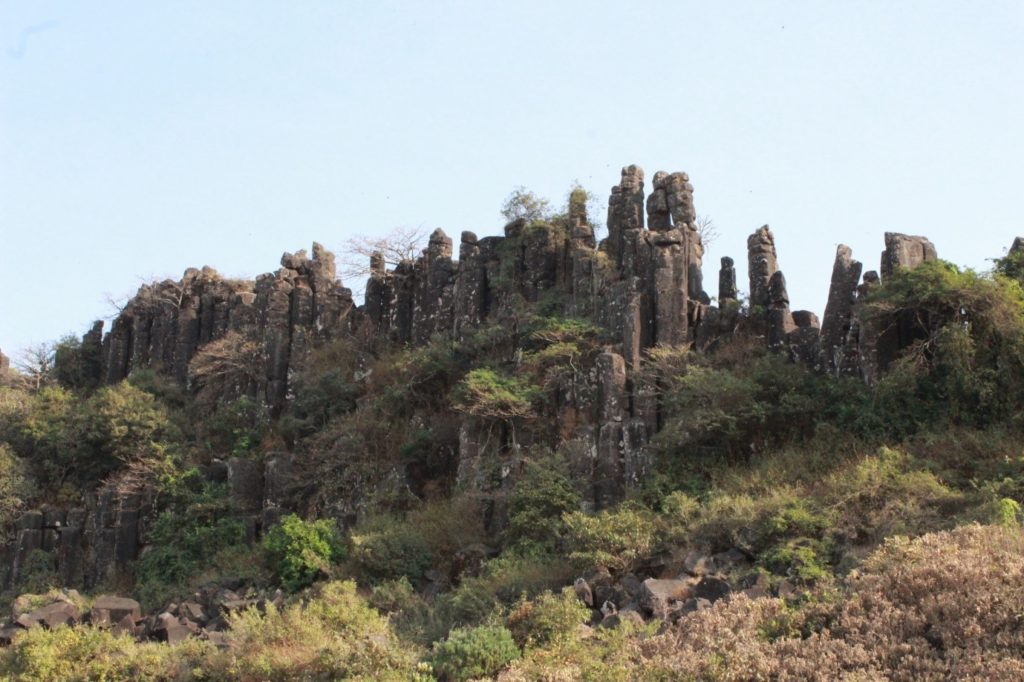

The newly discovered basalt flow with columnar structures is part of the 65.6 million-year-old Panhala Formation, one of the youngest formations of the Deccan Traps.
The series of spectacular columns of different sizes were found at Bandivade village near Panhala by researchers from Savitribai Phule Pune University, Dr. D Y Patil Vidyapeeth, Pune and Kolhapur-based D Y Patil College of Engineering and Technology and Gopal Krishna Gokhale College.
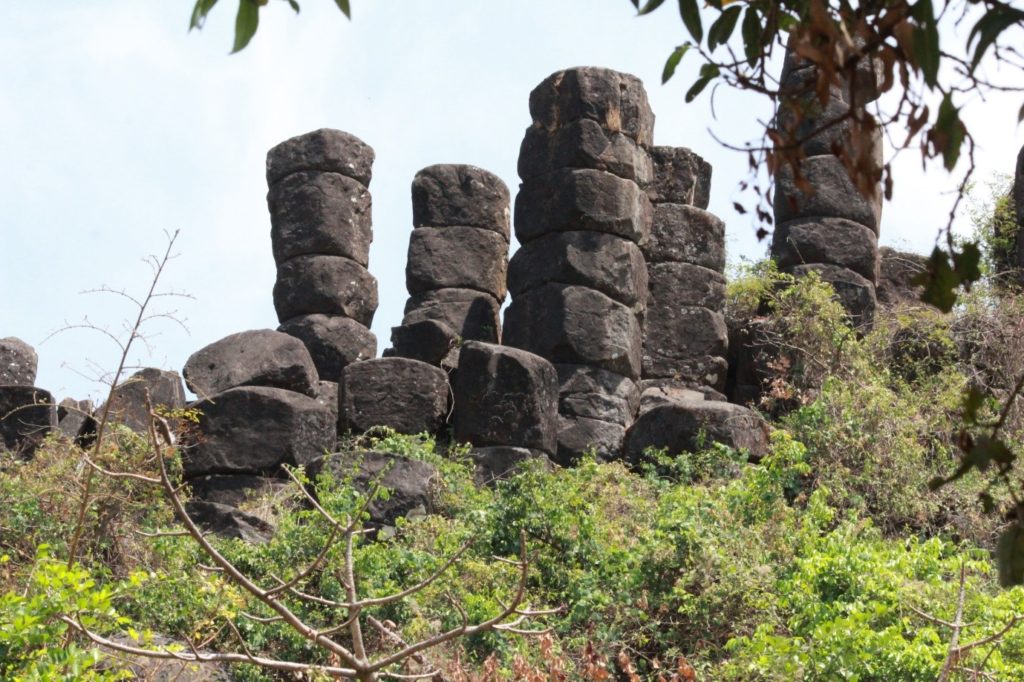

The basalt columns are present in different stages of disintegration. They rise above an east-west oriented low ridge (about 850 meters above sea level), connecting two laterite-capped tablelands.
The 80 to 90 meters thick columnar basalt flow occurs below the laterite, consisting of massive pentagonal columns. The diameter of the pentagonally shaped columns is about one meter. The isolated standing columns of different heights from 1 to 10 meters are also observed in the field.
“The discovered site is unique and remarkable. The spectacular polygonal columns got formed due to weathering and erosion of massive columnar basalts. Tall, majestic columns are in different stages of disintegration.
The site deserves to be recognized as a geo-heritage site and should be declared as a National Geological Monument,” suggested Dr. K D Shirke, the lead researcher, while speaking to India Science Wire.

Deccan Traps are the basaltic lava flows of Cretaceous to Eocene age in the geological timescale. It is the most extensive lava formation of Peninsular India covering an area of about half a million square kilometers extending over large parts of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Gujarat and some parts of Telangana and Karnataka.
The formation of Deccan traps started about 66.25 million years ago. A series of volcanic eruptions occurred there over a period of 30,000 years. Deccan Traps characteristically show horizontality of lava flows, development of flat-topped hills and step-like terraces. Thin but extensive red-boles separate these horizontal lava flows.
According to the researchers, the well-developed columns separated from each other with the upper horizontal capping of laterite are common in the Deccan flow in Central India but are rare in the nearly two km thick lava flows of Western Ghat escarpment. In Bandivade, the columns are well developed and stout than other sites like the Giant’s Causeway in Northern Ireland and St Mary’s Islands in Karnataka.
The Panhala site is very significant and a potential site for further geological studies. More studies are needed to understand site-specific characteristics of basalt flows and geomorphic factors responsible for differential weathering and erosion.
The research team included K D Shirke, J D Patil, K. Bandivedkar, N. Pawar and Vishwas S Kale. The results of the study have been published in journal Current Science. (India Science Wire)
By Dr. Ravi Mishra
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for the latest Science & Tech news. You can also find us on Twitter & Facebook.