Veterinary Drug May Be Repurposed For Human Cancers
- News
- 7.4K
Indian scientists have found that fenbendazole, a broad-spectrum antiparasitic drug used in the veterinary sector, could be useful against cancers as well.
Researchers at the National Centre for Human Genome Studies and Research (NCHGSR), Panjab University, have reported that fenbendazole has a good potential for development as an effective anti-cancer agent.
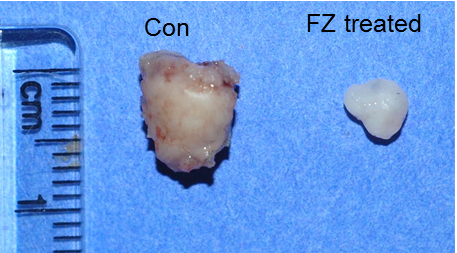
Reduced tumour size in mice fed with fenbendazole for 12 days
It is currently used as used to treat infections caused by parasitic worms in animals like horses. The study results have been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
To check the effectiveness of fenbendazole, researchers first treated human ‘non-small cell lung cancer cells’ (a type of lung cancer cells) with fenbendazole and analyzed cancer cells with the immunofluorescence technique.
They found that the drug causes partial alteration of microtubule network around the cell nucleus. Tumor cell lines also showed enhanced cell death-inducing activity in the presence of wild-type (WT) p53 tumor suppressor genes.
Researchers tested fenbendazole in mice, feeding them the drug orally every second day for 12 days. After the end of 12th day, tumors were excised, measured and weighed.
Researchers found a reduction in tumor size and weight. Results suggested that fenbendazole inhibits tumor cell growth in vivo by inducing apoptosis of tumor cells.
Cancer cells are known to show increased glucose uptake for their energy requirements. So, researchers tested the effect of fenbendazole on glucose uptake in human cancer cells. Two different type of cancer cells, H460, and A549 cells were treated with fenbendazole. Researchers found inhibition of glucose uptake in both the cell lines
According to researchers, fenbendazole may also be advantageous in evading drug resistance commonly encountered in cancer therapy. Since the process of tumorigenesis involves a number of genes and proteins altering various cell signaling pathways, single-target drugs often show limited efficacy and may lead to drug resistance.
Drugs having multiple cellular targets, therefore, are expected to have improved efficacy besides the ability to circumvent the likelihood of developing resistance.
“Our findings show that fenbendazole acts through moderate microtubule disruption, p53 stabilization, and interference with glucose metabolism leading to the preferential elimination of cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo”, explained Dr. Tapas Mukhopadhyay, former director, NCHGSR, who led the study, while speaking to India Science Wire.
The use of microtubule-targeting agents (MTAs) for the treatment of multiple tumor types is very common but their effectiveness is often hampered due to drug resistance.
“Usually, development of new drugs requires a considerable amount of time, money and effort. Developing a promising molecule into an approved drug often takes several years. It is, therefore, crucial to employ strategies to overcome these impediments.
Repurposing of veterinary drugs showing promising results for human use can result in considerable time and cost reduction required to develop new drugs,” said Dr. Mukhopadhyay.
According to the researchers, fenbendazole is known for a high safety margin and most species tolerate it very well. It has a very low degree of toxicity and a high degree of safety in experimental animals. Hence it can be a good candidate for anticancer therapy. Alternatively, it can also be used as an adjuvant therapy.
“FDA, as well as other published pre-clinical data on the toxicological studies performed on animals, shows that fenbendazole administered in different species at dosages several times the approved dosage does not cause any adverse effects in animals. Further, our previous study also showed minimal toxicity of fenbendazole in normal human cells. Considering this information, FZ can be an ideal candidate for development as an anti-cancer agent”, added Dr. Mukhopadhyay.
Besides Dr. Mukhopadhyay and Dr. Ashok Kumar from Panjab University, the research team included Dr. Nilambra Dogra from Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh. (India Science Wire)
By Yogesh Sharma
Journal Article [Image Wikimedia Commons]
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for the latest Science and Tech news. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.


