Fire Load of Buildings on the Rise According To a New Study
- News
- 2.3K
A new study by researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology, Gandhinagar, has warned that the fire load in modern day buildings in India is three times greater than what was even as late as the 1990s.
In the last few decades, lifestyles have changed significantly due to changes in socio-economic and cultural factors, resulting in newer office and residential cultures and luxuries. Modern-day buildings sport corrugated plastic roofs, partition walls, plastic doors, false ceiling panels, interior finish material, and have equipment like washing machines, refrigerators, air-conditioners, televisions, mobile electronic gadgets and computer hardware.
These new amenities have, no doubt, made life easier. However, they also pose higher fire risk since many of them are made of a material that has higher calorific values and thus more inflammable. For instance, paperwork has given way to digital records in offices and homes. This has meant that less cellulose and more plastic, which has higher calorific value, is being and stored and used. Though agencies involved in fire safety are aware of this, there is not much data available.
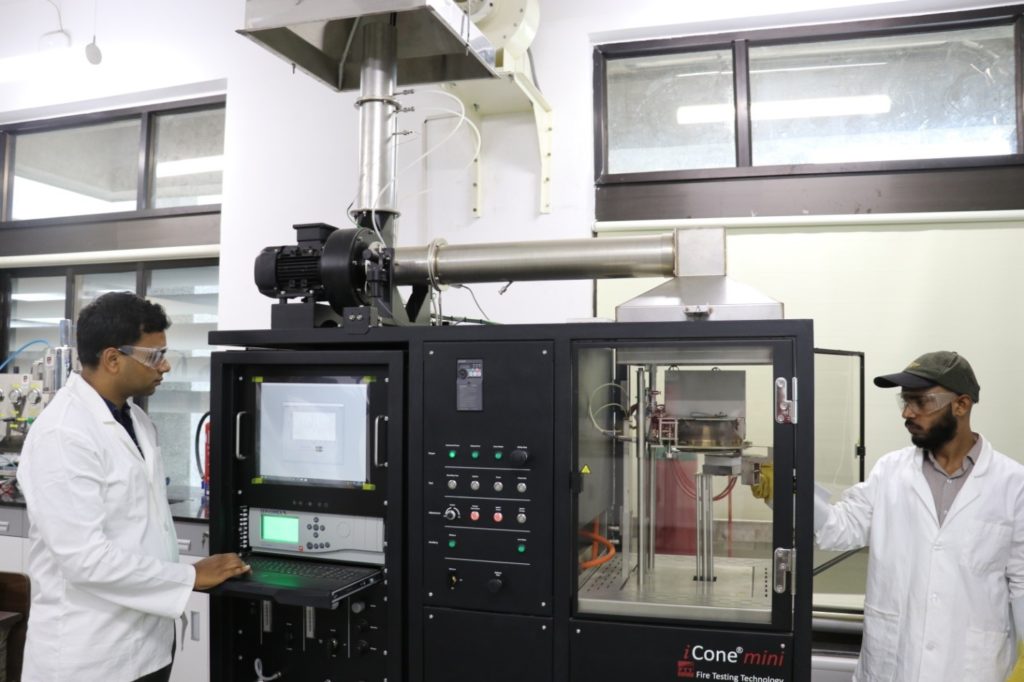

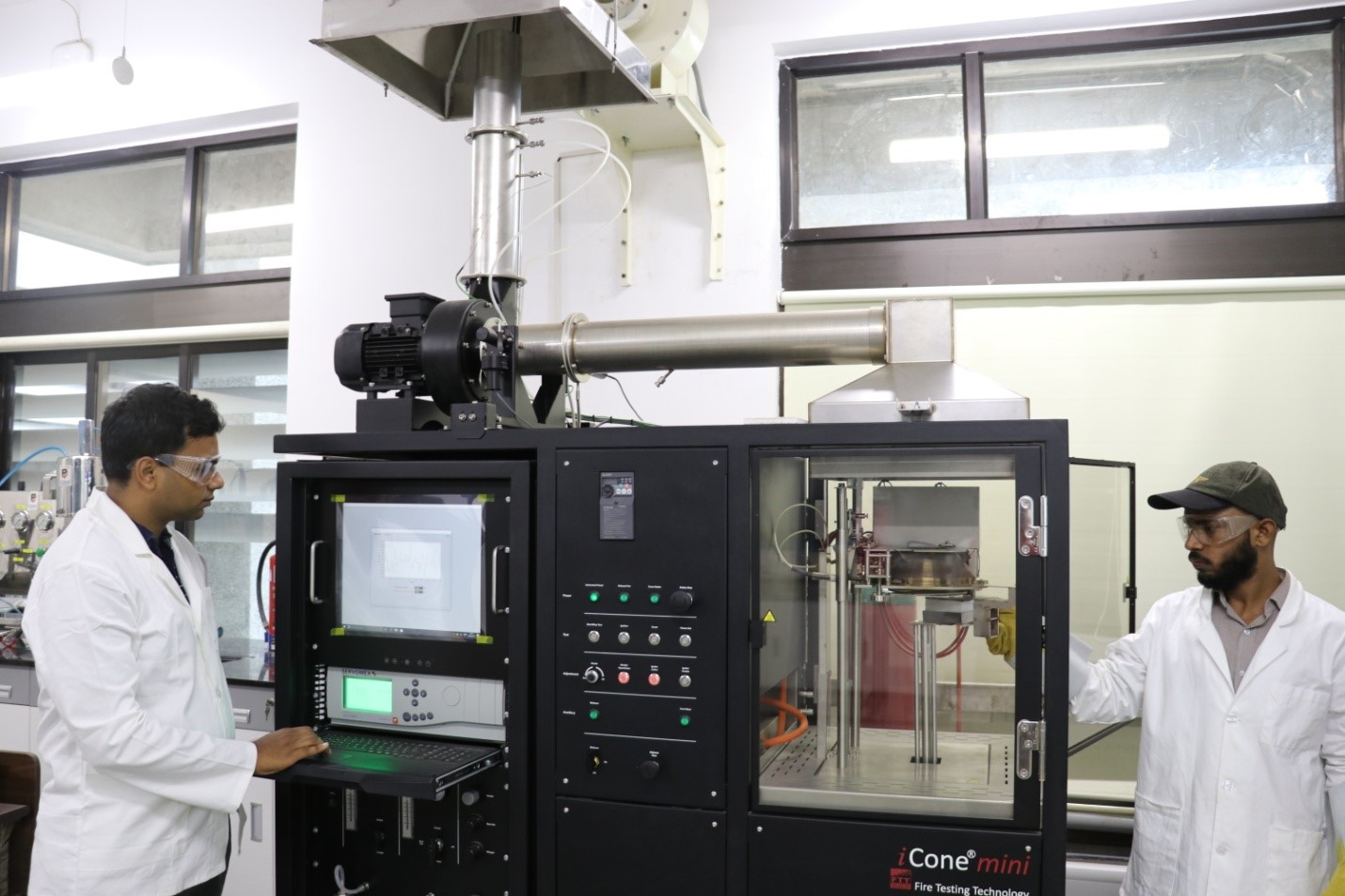
Dr. Gaurav Srivastava and Nasar Ahmad Khan in their laboratory with a Cone Calorimeter, which is used to measure combustion properties of materials
The researchers conducted a detailed survey covering a total of 105 office rooms and 202 students’ dormitory units in Ahmedabad. They found that average fire load energy density (FLED), which characterizes fire loads of these units, was found to be around 1400 Mega Joules per square meter, which is about three times the average of 487 MJ/ sq. m found during a study done conducted just 20 years ago in Kanpur. The maximum expected temperatures in the first one hour were also much higher than in the previous study.
Gaurav Srivastava, Assistant Professor at the Department of Civil Engineering at IIT-Gandhinagar, who conducted the study along with research scholar Nasar Ahmad Khan, said there was a need for thorough review of certain aspects of the Indian standards for fire safety, which are presently based on data obtained in the 1970s and 1980s.
“Safety of buildings depends on ensuring that the temperatures of their structural components remained below critical levels. The components are given fire ratings as per the expected critical temperature levels. We have found that the level of severity of fires as also maximum temperatures in the first hour has gone up substantially. That’s why there is perhaps a need to relook at fire rating in the standards,” Srivastava explained while speaking to India Science Wire.
The researchers found that cellulosic materials (wood and paper) accounted for the maximum proportion among all the combustibles at 54-69 %, followed by plastics (18-22%), textiles (7-8 %) and leather (4-6 %) for office rooms; and textiles (26-35%), plastics (6-8%) and leather (2-3%) for dormitories.
In the earlier study, cellulose material was almost the only combustible material in office and residential buildings at 98.6 percent. The study has been published in journal Current Science. (India Science Wire)
By Sunderarajan Padmanabhan
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for the latest Science and Tech news. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.