Low Cost Prosthetic Knee Joint Coming Soon
- News
- 2.6K
Locomotor disability is a significant problem in India, with an estimated one percent of the population suffering from it. Of them, 7.7 percent are transfemoral amputees. Transfemoral amputation also known as ‘above knee amputation’ is a surgical procedure performed to remove the lower limb above the knee joint when that limb has been severely damaged or diseased.
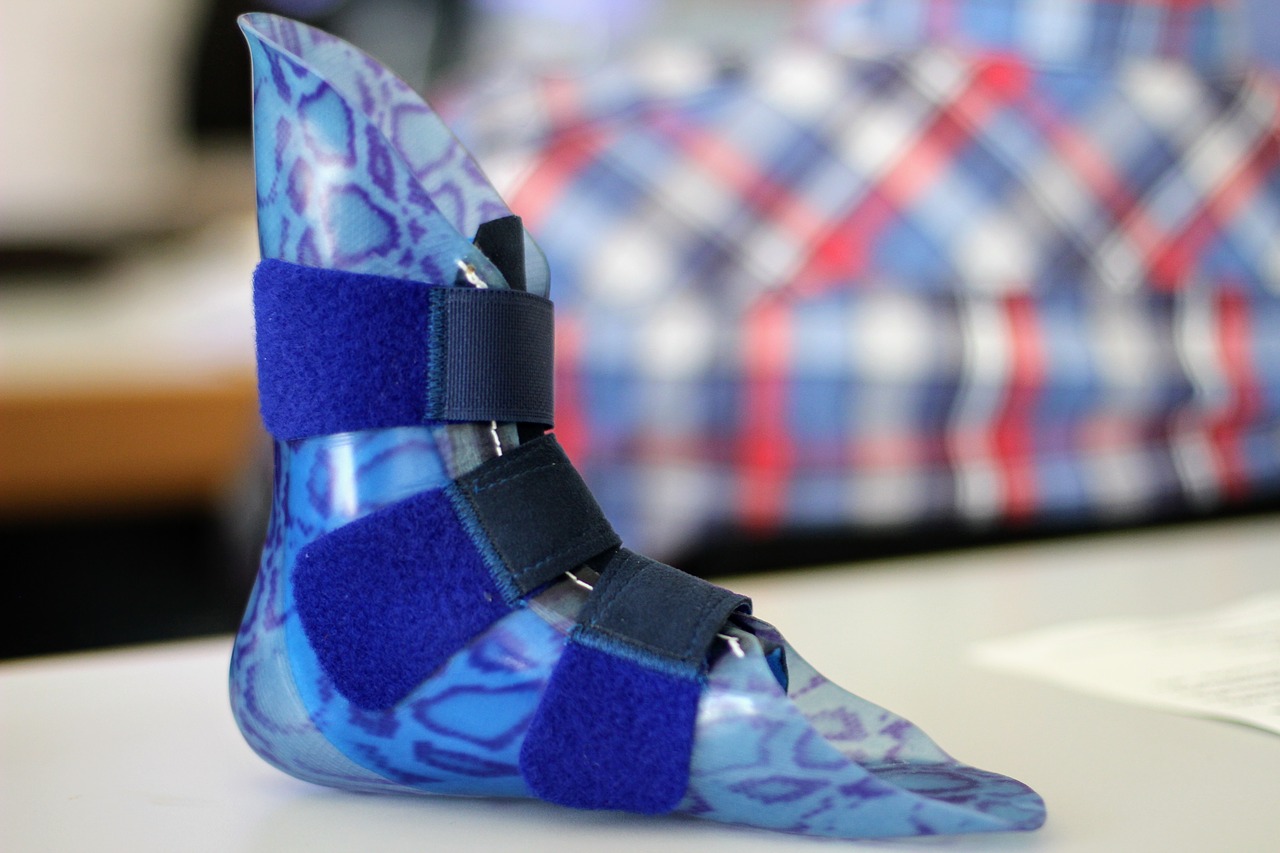
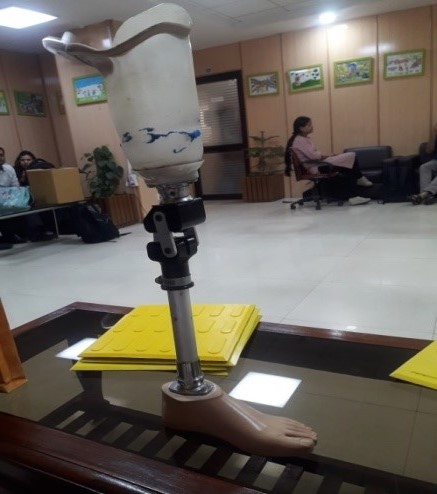
In order to alleviate the suffering of such people, researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi have designed and fabricated a low-cost, and light-weight polymeric polycentric prosthetic knee joint with energy-efficient gait option.
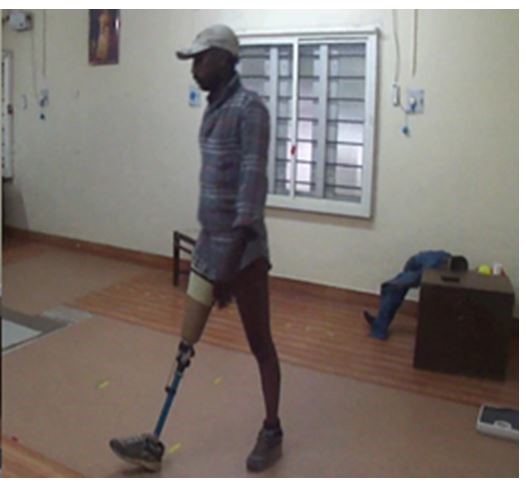
Patient walking with a prosthetic knee joint
The prosthetic is made up mainly of polymeric material through injection molding technique and is polycentric in design consisting of an upper part, a lower part with pylon adaptor, a middle bar, a sidebar and connecting bolts. It weighs a mere 350 grams.
The upper and lower parts are made of plastic material and the side and middle bars are made of aluminum alloy with a high strength-to-weight ratio. The side and the middle bars transfer the total weight of the body from the upper part of the knee joint to the lower part during single limb stance phase.
The prosthetic has multiple articulations with four axis points being the most common configuration. Since the four axes are connected by four linkage bars, this type of polycentric knee is also called four-bar knee.

Polycentric designs offer several biomechanical advantages and, as a result, are increasingly popular. A key distinction is that the functional center of rotation is generally located outside the knee joint, which provides inherent stability due to long leverage. In the four-bar knee, the instantaneous center of rotation (ICOR) can be determined geometrically by drawing straight lines through the posterior and anterior axes.
The point in space where they intersect is the instantaneous center of rotation. “ICOR is an imaginary center of rotation at the time of movement it rotates from extension to flexion from one place to another,” explained Prof Naresh Bhatnagar, lead researcher, while speaking with India Science Wire.
The researchers took seven years to come up with this knee joint design. It has been tested clinically at Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Government Medical College, Thiruvananthapuram.
Nine patients with unilateral transfemoral amputation and who could walk a minimum of four meters were included in the study. All were given seven days of gait training for adaptation of design before obtaining the gait data using BTS Smart DX Computerized Gait Analyzer.
“The result showed that the patient using the new prosthetic walked closer to natural gait pattern compared to the conventional ones. The energy expenditure was also reduced,” said Dr. Ranjeet Kumar, Research Scholar at IIT Delhi, who was also involved in the study along with another colleague Dr. Puneet Mahajan.
This technology was showcased at a recently held meeting at Technological Interventions for Disabled and Elderly (TIDE) programme of the Department of Science and Technology. (India Science Wire)
By Jyoti Singh
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for the latest Science and Tech news. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.