C V Raman Fellowships Bring African and Indian Researchers Closer
- News
- 1.6K
At the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) here, Abdelkarim Dafalla Elfadil from Sudan is working on a new mechanical device which will help sowing of seeds, irrigate fields and apply fertilizer in one go, using technology developed at the institute’s division of agricultural engineering.
Elfadil is working in India as a C V Raman Fellow. “Our target is to help him develop the machine before the six-month fellowship duration comes to an end. We are working very fast to reach that goal,” said Indra Mani, head, division of agricultural engineering. The device, he says, will go a long way in improving agriculture potential of arid zones in Sudan.
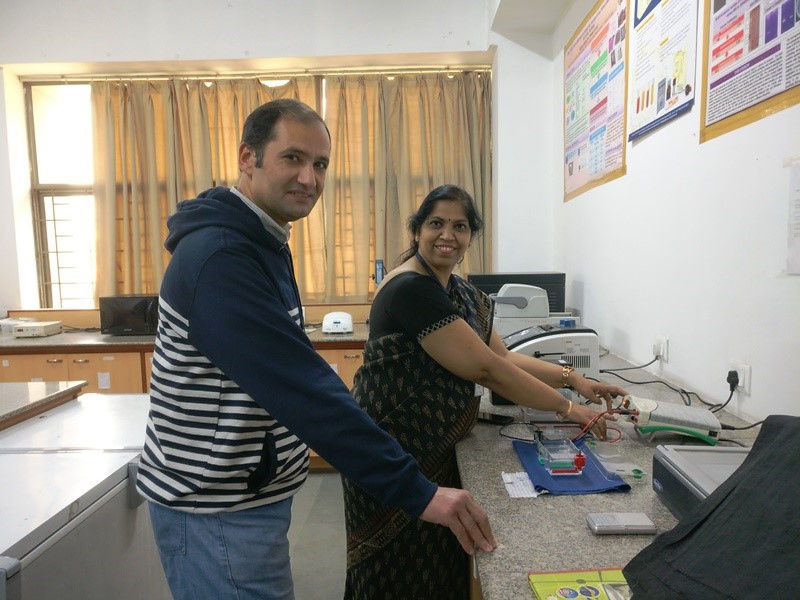

Gad with Dr. Rajni Singh
The ‘aqua ferti seed drilling’ is a mechanized sowing device capable of multi-tasking. The fertilizer distributed through the drill is in aqueous form, which facilitates timely irrigation and subsequent seed germination. “Elfadil is working on the same technology but is customizing the mechanism to the conditions of his country, keeping in mind soil, crop and water requirements,” said Mani.
This knowledge sharing exercise is part of the C V Raman International Fellowship programme for African researchers being implemented by the Department of Science and Technology (DST). Between 2010 and 2018, the number of African researchers who have availed the fellowship is close to 500. The number of Fellows during 2017-2018 is about 100.
Recently, DST and the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI) launched a coffee table book on the fellowship programme. It focuses on the successful journey of the programme so far. “The Fellowship is one of the most prestigious programmes of DST and we are proud to see the pan-India and Africa reach with our commitment to double up the number of fellowships,” said Prof. Ashutosh Sharma, Secretary, DST.
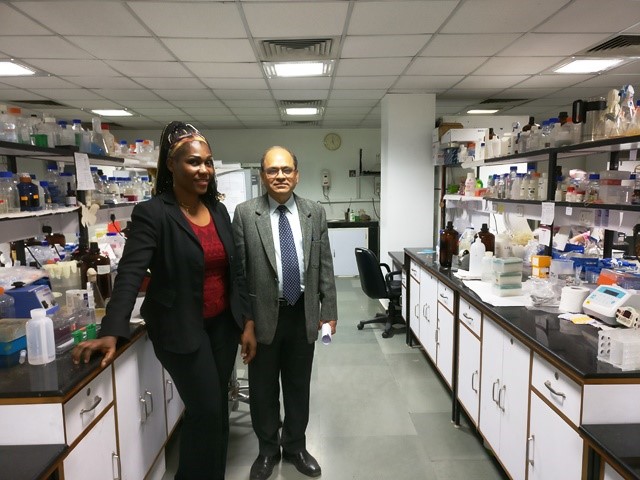

Isitua with Dr. Rakesh Bhatnagar
African fellows are aiming to use their training, gained through collaborative research in Indian universities as well as science and technology institutions, in various ways. They intend to publish papers in prestigious scholarly journals, engage in further research and improve the quality of lives back home.
The fellowship that offers opportunities for training for a period ranging between four weeks and six months is gaining popularity in Africa since its launch in 2010. African scholars attribute this success to positive research environment in India. For instance, Chinwe Christy Isitua from Nigeria is working under Dr. Rakesh Bhatnagar at School of Biotechnology, Jawaharlal Nehru University’s (JNU). Isitua had applied for the fellowship thrice and has managed to get it only on her last attempt.
Isitua, associate professor of microbiology at Nigeria’s Afe Babalola University (ABUAD), has already picked up conversational Hindi phrases such as suprabhat. She is upbeat about her research on the role of indigenous African spices in inhibiting proliferation of cancer cells. “I will use the knowledge acquired in India to add value to the learning of my students at ABUAD,” said Isitua.
Indian scientists hosting African researchers agree that the three categories – Doctoral/Post Doctoral, Visiting Fellowship and Senior Fellowship – offered under the programme has strengthened research ties between Africa and India.
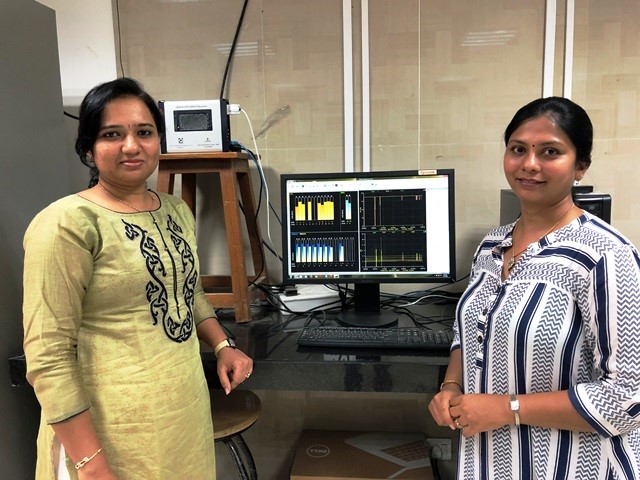
Gad Elsayedmohamed Salem, a researcher at Egypt’s National Organization for Drug Control and Research (NODCAR) and currently a C V Raman Fellow at Amity Institute of Microbial Biotechnology, said everyone at his host institute was a collaborator. The Egyptian researcher’s work in the domain of fibrinolytic enzymes is closely linked to the work of his host scientist, Dr. Rajni Singh, on microbial enzymes and microbial biotechnology.
“Gad wasn’t aware of purification techniques of particular enzymes, which he learned during his stint here. He also got to know about ways to use different microbial cultures and handle them,” said Dr. Singh.
A reason why the fellowship has created a buzz among African researchers is that their assimilation in Indian universities and research facilities is smooth. For many African scholars, a welcoming environment is a big draw. According to Salem, his fascination with Delhi stemmed from the city’s abundant greenery. “Through my interactions with Indian people I found them to be polite, cooperative and peaceful,” said Salem.
Equally positive is Mustapha Jamma of Morocco, who is availing the fellowship at Delhi Technological University under Dr. Dheeraj Joshi. Jamma has been encouraged to visit various laboratories within the campus so as to get maximum exposure through interactions with the institute’s M. Tech and Ph.D. students. “We keep the laboratory where he is working open till 8 pm so that he gets uninterrupted research time. His accommodation facilities have been arranged within the campus at a reasonable price. Jamma is so optimistic about the Indian research eco-system that he has extended his fellowship duration by one month,” said Dr. Joshi, Professor, Electrical Engineering Department, Delhi Technological University. (India Science Wire)
By Susmita Saha
For the latest Science and Tech news and conversations, follow Research Stash on Twitter, Facebook, and subscribe to our YouTube channel


