Research Stash Weekly Round Up #9
- Weekly Review
- 1.8K
Zika Virus Infects Developing Brain by First Infecting Cells Meant to Defend Against It
Researchers at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine, with colleagues in Brazil, report that the Zika virus is transmitted from mother to fetus by infected cells that, ironically, will later develop into the brain’s first and primary form of defence against invasive pathogens. Read More
More Cardiac Arrest Victims Could Survive With Dispatcher CPR Instruction, Rescue Breaths For Children
More people will survive cardiac arrest if emergency medical dispatchers give chest compression-only CPR instructions over the phone and if infants and children receive chest compressions with rescue breaths, according to updated CPR guidelines published today by the American Heart Association (Association) Read More
Why the sounds of eating make some people so angry

Nobody likes hearing someone crunching their food, but for some, it’s more than just an annoyance — the sound triggers a full “fight or flight response.” These people have a rare condition called “misophonia” that makes them extraordinarily sensitive to everyday sounds Read More
Penn Study Shows Nearly 70 Percent Of Cannabidiol Extracts Sold Online Are Mislabeled

In recent years, there has been an increased interest in the medicinal use of Cannabidiol (CBD), a chemical that naturally occurs the in cannabis plant (aka “marijuana”). There is interest in CBD as a medicine because there is some evidence that it has medical benefits Read More
‘Zombie ant’ brains left intact by fungal parasite
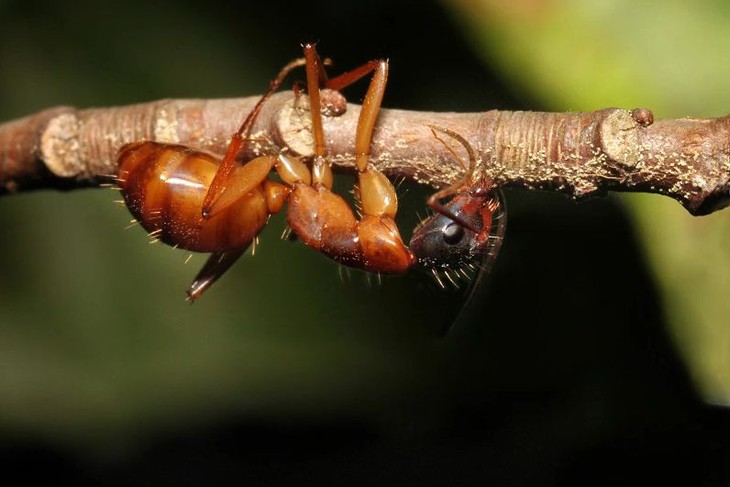

A fungal parasite that infects ants and manipulates their behaviour to benefit the fungus’ reproduction accomplishes this feat without infecting the ants’ brains, according to a study led by Penn State researchers. Read More
Eating at night could increase risk of heart disease and diabetes

Eating during the night is associated with higher risk of heart disease and diabetes, and the body’s 24-hour cycle is to blame, according to research published today in Experimental Physiology. Read More
How a “flipped” gene helped butterflies evolve mimicry
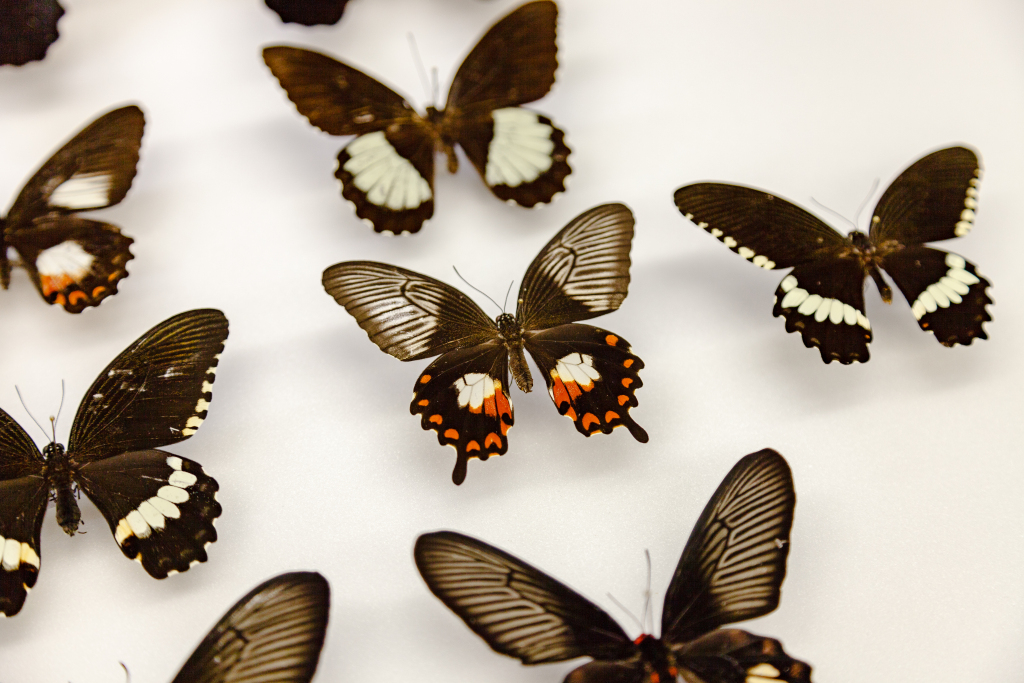

Female swallowtail butterflies do something a lot of butterflies do to survive: they mimic wing patterns, shapes and colours of other species that are toxic to predators. Some – but not all – swallowtail species have evolved several different forms of this trait. Read More
Researchers Teach Computer to Recognize Emotions in Speech
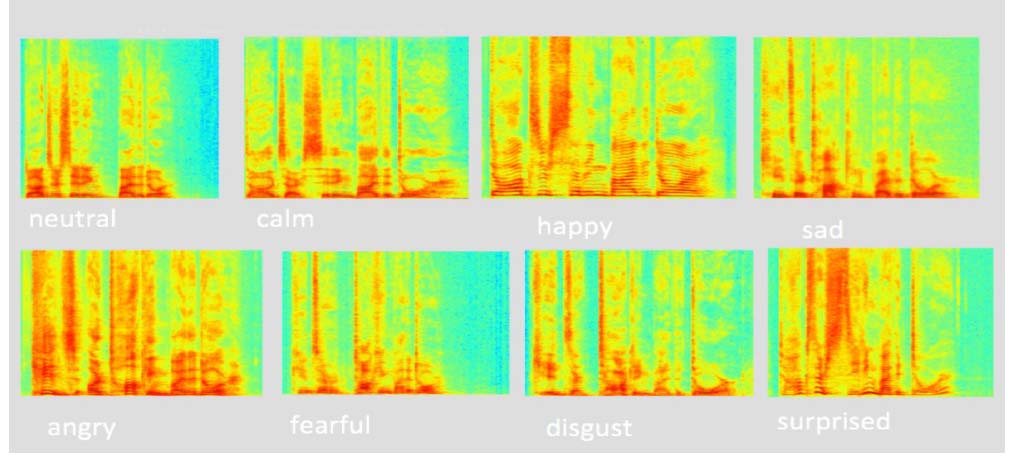
Staff Members of the Faculty of Informatics, Mathematics, and Computer Science at the Higher School of Economics have created an automatic system capable of identifying emotions in the sound of a voice. Their report was presented at a major international conference – Neuroinformatics-2017. Read More
NASA Twins Study spots thousands of genes toggling on and off in Scott Kelly

When astronaut Scott Kelly returned to Earth after a year floating about the International Space Station, he was noticeably different from his identical twin, Mark Kelly. Read More
Cancer cells destroyed in just 3 days with new technique
Cancer cells are relentless, possessing the vexatious ability to develop resistance to current therapies and making the disease hugely challenging to treat. However, an exciting new study may have identified cancer’s weak spot; the discovery has already led to the near-eradication of the disease in cell cultures. Read More
Enjoyed reading latest news in S.T.E.M? Follow Research Stash for latest updates