Understanding Positioning System of Cells May Help Unravel Key Diseases
- News
- 1.9K
In our day to day life, a global positioning system (GPS) helps us quickly determine our location and guides us to a preferred destination. Similarly, in living cells, molecules like proteins have their own positioning system which guides cells to coordinate their functioning and ensures a response. There is constant cross-talk among molecules in different compartments of the cell through such a positioning system.
Indian researchers are studying this positioning system in proteins like RDGB which ferry and move lipid molecules to maintain homeostatic levels of lipids in the plasma membrane. An understanding of how molecules like RDGB control lipid composition may help to get an insight into complications that lead to cancers and neurodegenerative diseases.

A team of researchers led by Dr. Padinjat Raghu at National Centre for Biological Sciences, Bengaluru have shown that signals present within RDGB protein determine if it will remain in a specific compartment of the cell for it to function normally. “This is important since, in the absence of such localization, the cellular function of this protein will be compromised,” researchers say in their study published in the Journal of Cell Science.
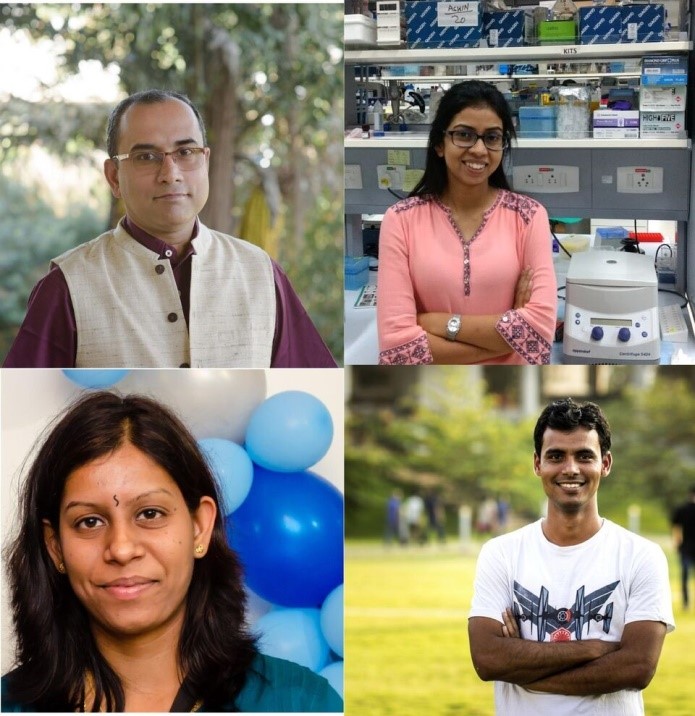
“RDGB is known to localize at a specific location in the cell to maintain lipid composition of two closely situated membranes by transferring lipids from one compartment to the other. We want to understand how this process might be regulated,” pointed out Rajan Thakur, co-author of this study. The work has been done in fruit fly which has a simpler genome makeup and shares much of the organizational principles of human cells.
Cells have thousands of molecules like proteins, lipids and carbohydrates and others, and still, every function is perfectly executed with respect to time, distance and their location. The new study explains that though different cellular structures perform specialized functions in seclusion, they do exchange information with each other to shape the signaling output of the cell.
“In the absence of correct localization of RDGB protein to a unique part of the cell, the photoreceptor cell does not function normally and fails to respond to light. We have found some key parts of the cellular positioning system that help in correct localization of RDGB protein,” said Dr. Raghu.
According to the study, cells have evolved ways to meet the requirement of organisms. For instance, specialized cells like photoreceptors have to process information over a large range of stimuli, from dim to very bright light. “These cells transduce the visual information at a fast pace by sequestering proteins near the light-sensitive membrane through robust positioning system,” said Shweta Yadav, first author in this study.
Dr. Raghu said, “We have discovered in fruit fly one key component of the positioning system that localizes RDGB is the protein, VAP. Mutations in human VAP have been identified in cases of the neurodegenerative disease called Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS).” He said this study might provide new insights into why patients with ALS undergo neurodegeneration leading to possible treatments.
The research team included Shweta Yadav, Rajan Thakur Harini K and Padinjat Raghu (NCBS, Bengaluru); P. Georgiev (Babraham Institute, United Kingdom); S. Deivasigamani and G. Ratnaparkhi (IISER,Pune). (India Science Wire)
Journal Article
RDGBα localization and function at a membrane contact site is regulated by FFAT/VAP interactions http://bit.ly/2AJJ4aS