Research Stash Weekly Review 5
- Weekly Review
- 1.6K
New gene mutations found in white blood cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Gene mutations accumulating in cells are typical of the development of cancer. Finnish researchers found that a similar accumulation of mutations occurs also in some patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Read More
Using ‘sticky’ nanoparticles, researchers develop strategy to boost body’s cancer defenses

After radiation treatment, dying cancer cells spit out mutated proteins into the body. Scientists now know that the immune system can detect these proteins and kill cancer in other parts of the body using these protein markers as a guide – a phenomenon that the University of North Carolina Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers are looking to harness to improve cancer treatment. Read More
Scientists use algorithm to peer through opaque brains

Trying to pinpoint signals from individual neurons within a block of brain tissue is like trying to count headlights in thick fog. A new algorithm, developed by researchers based at The Rockefeller University, brings this brain activity into focus. Read More
Being Forgetful May Mean Your Brain Is Actually Working Properly

A story making the rounds today is that being forgetful may be a sign of your brain working properly. Not remembering trivial details may actually be a sign your brain is better at separating the wheat from the chaff. Read More
Microneedle patches for flu vaccination prove successful in first human clinical trial
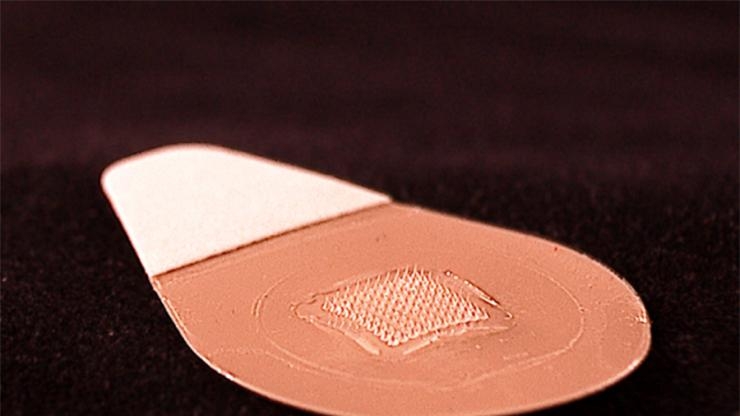
Despite the potentially severe consequences of illness and even death, only about 40 percent of adults in the United States receive flu shots each year; however, researchers believe a new self-administered, painless vaccine skin patch containing microscopic needles could significantly increase the number of people who get vaccinated. Read More
Scientists Have Uncovered The Atomic Structure of a Key Alzheimer’s Protein For The First Time
For the first time, scientists have revealed the chemical structure of one of the key markers of Alzheimer’s disease, capturing high-resolution images of the abnormal tau protein deposits suspected to be behind Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative conditions. Read More
Scientists say they have worked out why eggs are shaped like eggs

If a Hollywood exec dreamed up an egg, it would look like a chicken’s: immensely popular, with an unblemished complexion. But the universe of wild bird eggs is far weirder and more diverse than the oval products on the supermarket shelf. Hummingbirds lay eggs shaped like Tic Tac mints – “perfect little ellipses,” per ornithologist and evolutionary biologist Mary Stoddard. Read More
Scientific studies favor male mice—and that could hurt a lot of humans

The biological differences between men and women can affect the way they react to certain drugs and treatments, according to a new study in Nature Communications. If this sounds like a no-brainer, you probably haven’t looked at many biomedical studies. As PopSci noted earlier this year, biomedical researchers experiment almost exclusively on male animal subjects. A 2011 study found that animals in medical research are up to five times more likely to be male than female. Read More
DNA of soldiers with PTSD offers less protection against trauma

The DNA of soldiers who develop symptoms of PTSD after deployment to a war zone gives them less protection against traumatic experiences. Genetic material typically shows measurable changes after traumatic events. However, these changes are not or are barely seen in the DNA of soldiers who develop symptoms of PTSD. This is the conclusion of a comprehensive study conducted by an international group of researchers from the Dutch Ministry of Defence, University Medical Center Utrecht, Maastricht University and the Veteran Affairs Medical Center in collaboration with the University of California, San Diego. Their research results involving epigenetic changes in the DNA of soldiers exposed to war trauma were recently published in the renowned academic journal Molecular Psychiatry. Read More
The brain needs cleaning to stay healthy

Research led by the Achucarro Basque Center for Neuroscience, the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU), and the Ikerbasque Foundation has revealed the mechanisms that keep the brain clean during neurodegenerative diseases. Read More
Enjoyed reading these updates? Follow us on Facebook to stay updated about the latest news in Science and Technology