NSRRC – An advanced synchrotron source serving basic and applied research
- News
- 3.2K
“If only scientists gave us the technology to travel at the speed of light the solar system would be an open book.” – Unknown
“Light” has always been indispensable to man’s exploration of nature. All wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum can be referred to as “light”. “Light” of different wavelengths is used for different purposes. The longest wavelengths, radio waves, are used for observing the expansive universe, and microwaves are used to detect planes, ships, and typhoons.
Infrared Light is an ideal light source for night vision systems and the detection of missiles through tracking their heat sources. Visible light is the only wavelength humans can see with their naked eyes. Ultra-violet light is used to examine the structure of gas molecules and condensed matter. X-rays are the best source for researching crystal structures; and gamma rays, with the shortest wavelength, allow researchers to explore the inner world of atoms.
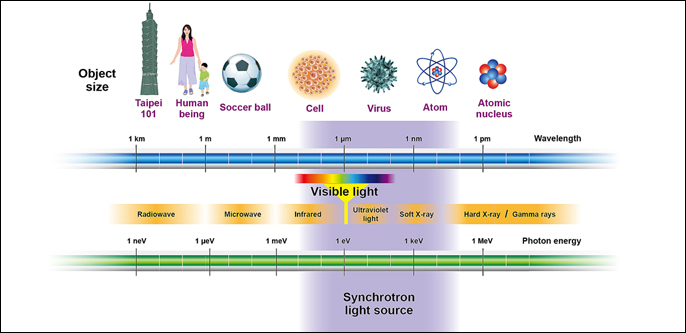
“Synchrotron radiation” refers to a continuous band of the electromagnetic spectrum including infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, and X-rays. This light has been called “synchrotron radiation”, since it was accidentally discovered in an electron synchrotron of the General Electric Company, USA, in 1947.
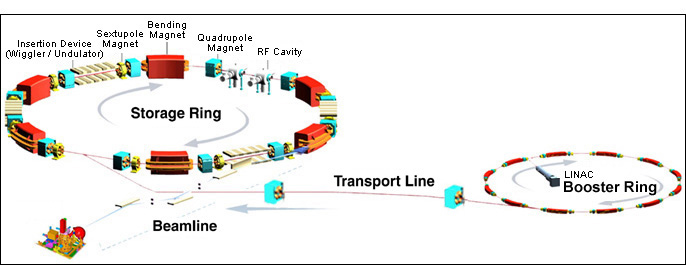
As part of the advanced light source, synchrotron radiation has become an important tool for use in diverse research fields such as physics, chemistry, biology, materials science, chemical engineering, environmental engineering, energy resources, mechanical engineering, and electronics. Over seventy synchrotron radiation facilities have been constructed worldwide with applications in scientific research and industrial R&D. National Synchrotron Radiation Research Center is one among them (NSRRC).
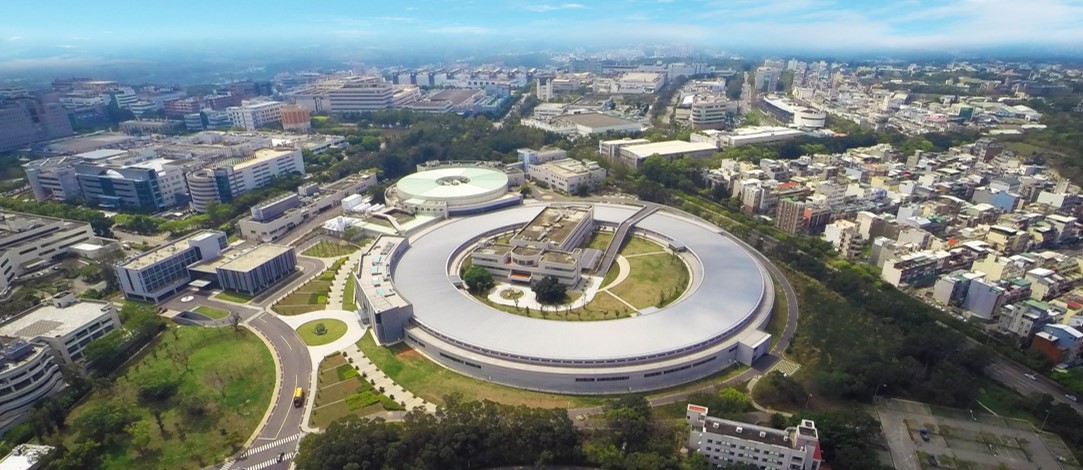

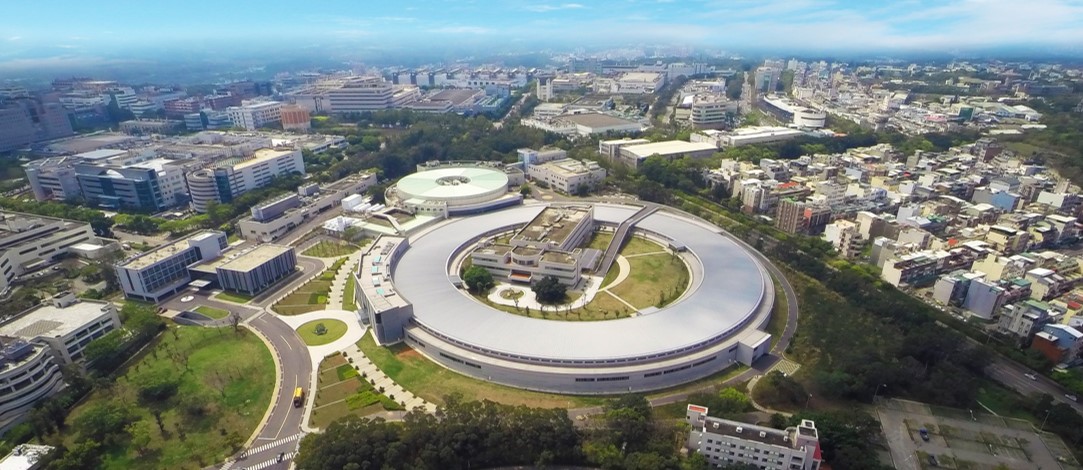
NSRRC’s mission is to operate a cutting-edge synchrotron radiation facility for pioneering scientific research. The light source at NSRRC was designed and constructed domestically and became operational in October of 1993. In April 1994, its beamlines were opened for service to researchers in diverse basic and applied fields.
In recent years, many new research instruments have been added to the light source, turning the center into a world-class facility with state-of-the-art research capabilities in the vacuum-ultraviolet and soft X-ray energy regions. In 1998, additionally, two hard X-ray beamlines were constructed at SPring-8 light source in Japan to provide researchers from Taiwan access to hard X-rays.
In order to satisfy the demands of researchers who require the use of the super high X-rays light source to facilitate their front-edge scientific experiments, NSRRC and the academic and scientific communities have conducted numerous discussions and assessments in recent years for the construction of a new synchrotron light source facility.
During the board meeting held on July 2004, it has been decided to bring up the proposal of Taiwan Photon Source cutting-edge experimental facility construction plan to the government to establish a new accelerator on the current base with an energy 3 billion electron volts of the electron beam and a circumference 518 meters, low emittance (Taiwan Photon Source) synchrotron light source facility. The ground-breaking ceremony for the civil construction of Taiwan Photon Source (TPS) was held on February 7, 2010. The civil construction has completed in 2014 and the light source and its experimental facilities are opened to the academic and scientific communities to conduct advanced research in 2016.
The TPS is the largest cross-field cutting-edge experimental facility in Taiwan. It offers one of the world’s brightest synchrotron X-ray sources, open numerous prospective scientific research opportunities, enhance world-class academic research to attain international competence, and assist the high-tech industry in improving its research and development capability while it creates Taiwan’s scientific research marvels in the twenty-first century.


