Research Stash Weekly Review 3
- Weekly Review
- 1.7K
Scientists Have Discovered Never-Before-Seen Vessels in The Brain

Scientists in the US have discovered a new series of lymphatic vessels in the body that link the brain to the immune system – a connection researchers had previously thought didn’t exist. The discovery could not only prompt a rewrite of the textbooks, it might also lead to a new understanding of how our immune system influences our brain and our behavior. Read More
Jupiter Now Has 69 Moons
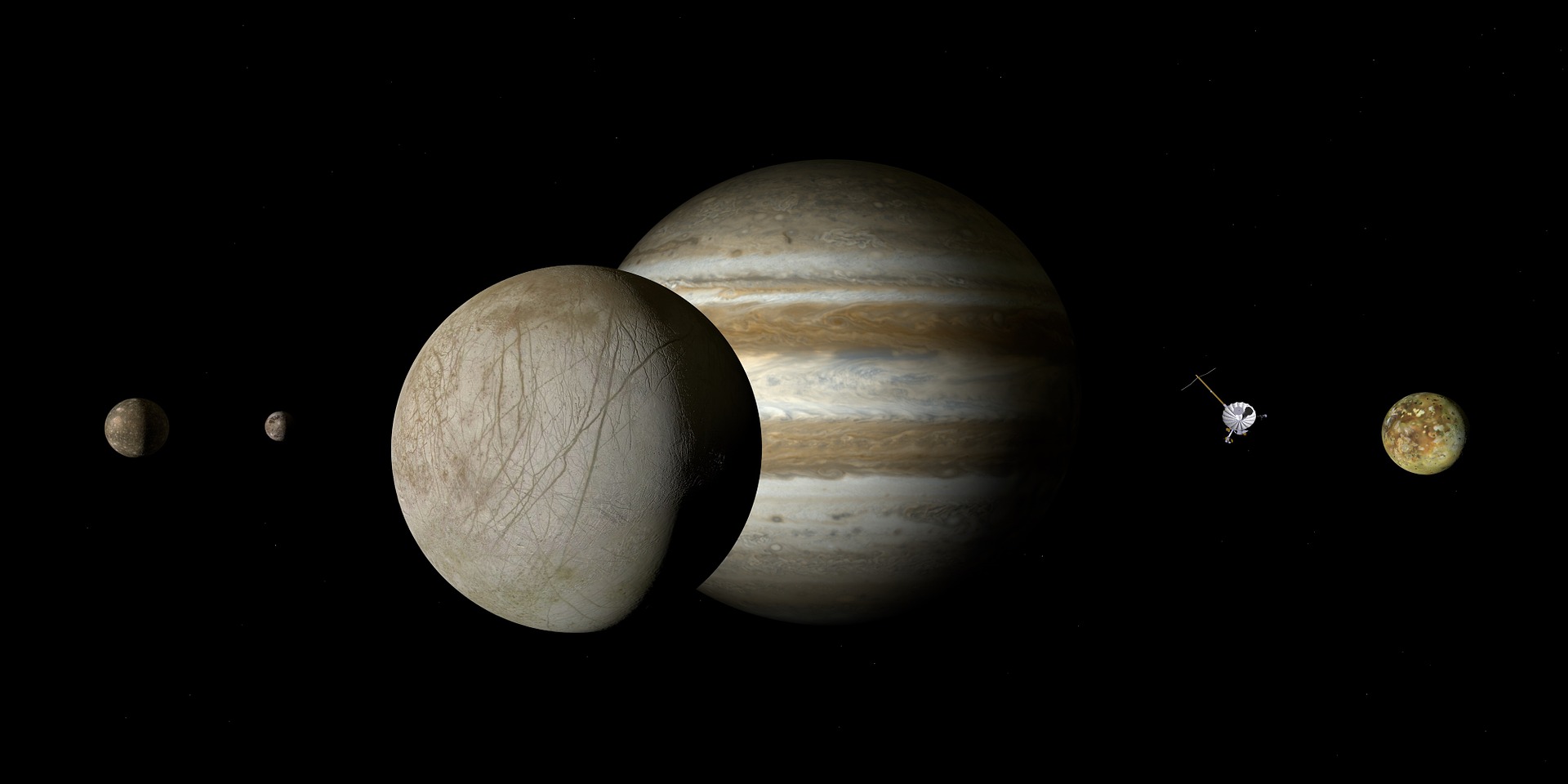

The planet Jupiter is a beast: Three-hundred-and-seventeen times the mass of the Earth, mostly made of metallic hydrogen, and at the center of an astonishing collective of orbiting natural bodies. Read More
This ‘Cyborg Rose’ Grows Functioning Electronic Circulatory Inside its Stem and Leaves
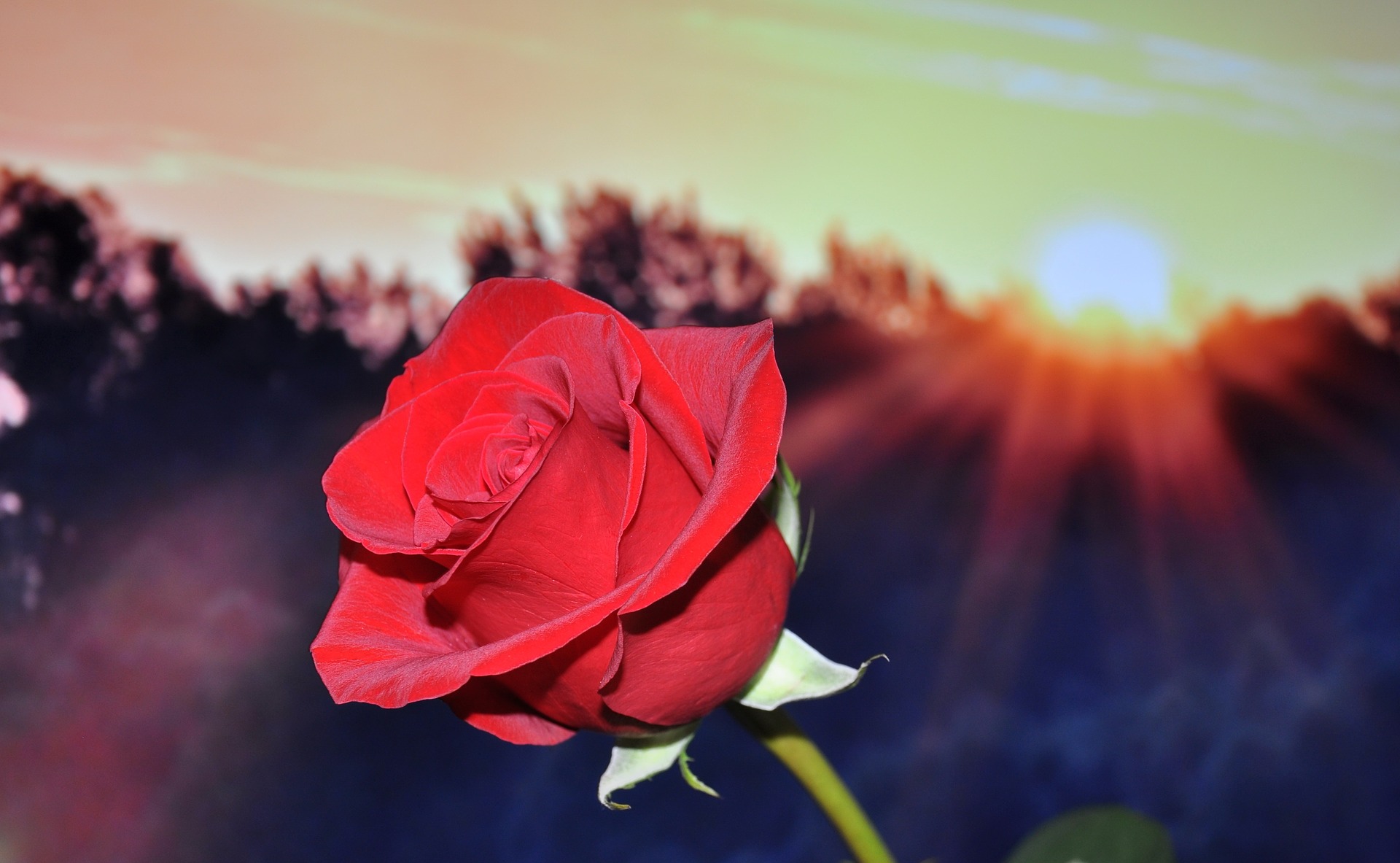

Scientists have figured out how to inject a conducting solution into a rose cutting, and have it spontaneously form wires throughout its stem, leaves, and petals to create fully functioning supercapacitors for energy storage. Read More
3-D printer creates blood vessel networks

Networks of blood vessels branch throughout almost every tissue of the body. These vessels are channels for the transport of blood cells, nutrients, and waste products. Researchers have made much recent progress in engineering new tissues and organs. However, creating functional networks of blood vessels to provide vital transport to the cells within these engineered tissues remains a major challenge. Read More
Graphene transistor could mean computers that are 1,000 times faster
A University of Central Florida professor is part of a research team that developed a graphene-based transistor that could someday lead to computers that are a thousand times faster and uses a hundredth of the power. Read More
Earth Faces an Increased Risk of Being Hit by an Asteroid, Astronomers Warn

Image: Thinkstock
A team of astronomers from the Czech Academy of Sciences announced the findings on Tuesday after studying the Taurid meteoroid stream. The stream produces a meteor shower that usually has a long period of activity in October and November and produces a low number of meteors. The meteors — light phenomena that are seen when a meteoroid enters the planet’s atmosphere and vaporizes, also referred to as “shooting stars” — occur when Earth’s orbit plows into the stream of debris left behind by Comet Encke. Read More
Scientists Have Identified What Caused Those Crazy Scars on Saturn’s Largest Moon

Mysterious streaks covering the surface of Titan, Saturn’s largest moon, could have been formed by freakish weather patterns and rainfall, according to new research.
These mazes of valleys, channels, and peaks have been puzzling scientists ever since they were first glimpsed by the Cassini probe back in 2004, and the satellite recently completed a more detailed map of the labyrinth-like terrain for scientists to study. Read More
New flu test: One drop of blood could save your life
The High-risk Influenza Screen Test (HIST) measures ‘an early warning signal’ released by the patient’s body into their blood to ‘kick start’ their immune system’s fight against the infection. The test needs only a single drop of blood and a few hours to predict, with 91 percent accuracy, which influenza patients will develop potentially deadly secondary infections, such as pneumonia. Previously doctors could only test for influenza infection but didn’t know which patients would be at risk of rapid deterioration. Read More
New blood test detects stroke and heart attack risk in lupus patients with no CVD symptoms

The results of a study presented today at the Annual European Congress of Rheumatology (EULAR) 2017 press conference have shown that a specific biomarker detected in the blood of lupus patients with no symptoms of cardiovascular disease(CVD), thought to be at low risk of CVDbased on traditional risk factors, is associated with the presence of atherosclerosis. Read More
Ebola vaccine developed in Canada shows promising results
A phase 1 randomized controlled trial has found an Ebola virus disease (EVD) vaccine, developed in Canada, was well-tolerated with no safety concerns, and high antibodies were present in participants 6 months after immunization. The study, led by Canadian researchers, is published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal). Read More
Images: Pixabay